Figure 2.
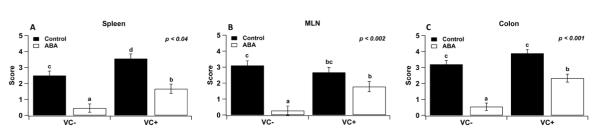
Effect of dietary abscisic acid (ABA)-supplementation on disease severity: a macroscopically evaluation. C57BL/6J mice were fed ABA supplemented (0.1 g/kg) or control diets for 35 days and challenged with 2.5% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in the drinking water for 7 days. On day 7, intestinal epithelial cell-specific PPAR γ null (VC+) and PPAR γ-expressing (VC−) mice fed ABA and control diets were euthanized, and colon, spleen, and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) were scored for inflammatory lesions. Significant effects (P<0.05) of the genotype (G) by diet (D) interaction are shown. Values are means ± SEM, n = 10. Means without a common letter differ, P<0.05.
