FIG. 8.
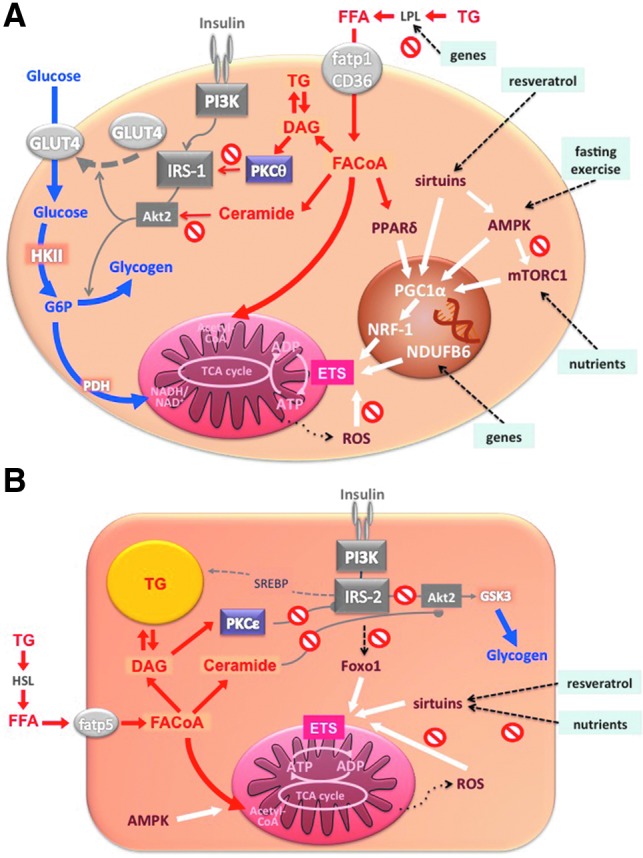
Potential regulators of mitochondrial biogenesis and function. In the myocyte (A), glucose is taken up via glucose transporter 4 (glut4), activated to glucose-6-phosphate (G6P), and then oxidized in the mitochondria or stored as glycogen. Free fatty acids are taken up via LPL and fatty acid transporter proteins (fatp1, CD36) and activated to fatty acyl coenzyme A (FACoA). FACoA can be oxidized in the mitochondria or stored as triglycerides or can favor the formation of diacylglycerols (DAG) and/or ceramides, thus inhibiting insulin signaling by protein kinase C-θ (PKCθ)/IRS-1 pathway and/or protein kinase B-2 (Akt2) phosphorylation, respectively. Both glucose and lipid oxidation fuel the tricarboxylic acid cycle and serve to produce ATP. Black dashed arrows represent genetic predispositions and lifestyle interventions affecting mitochondrial biogenesis/function via different mechanisms (white arrows): inherited factors associate with decreased LPL activity and PPARδ-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis; single nucleotide polymorphism of NDUFB6 gene predisposes to impaired mitochondrial plasticity in response to exercise; and resveratrol, fasting/exercise, and nutrients increase mitochondrial biogenesis/function by increasing PGC1α activity via sirtuins, AMPK, and mTORC1, respectively. ROS have been associated with decreased mitochondrial function. In hepatocytes (B), free fatty acids are taken up via fatty acid transporter protein 5 (fatp5), activated to FACoA, and undergo similar metabolic pathway as in the myocyte. Decreased activity of IRS-2 associates with lower Foxo1 and mitochondrial function. Resveratrol increases while overloading with nutrients decreases sirtuins and mitochondrial biogenesis. Finally, ROS impact negatively on the function of mitochondria. Acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; GSK3, glycogen synthase kinase 3; HKII, hexokinase II; HSL, hormone sensitive lipase; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase; SREBP, sterol regulatory element binding protein; TG, triglyceride. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars
