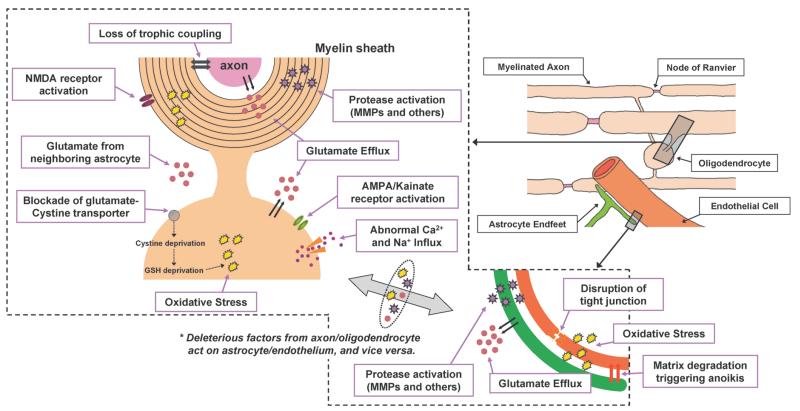
Fig. 3.
Schematic of the Adult White Matter under Stroke Conditions The main components of white matter are the neuronal axon, oligodendrocyte (myelin), astrocyte, and endothelium. Similar to gray matter, cell-cell interactions are important to maintain white matter function. Under ishemic conditions, several deleterious factors/cascades are activated. As in the neurovascular unit, several events occur due to ischemic stress. Glutamate efflux, oxidative stress, and proteinase activation eventually induce cell death. Importantly, deleterious factors secreted by one cell type may affect another cell type. For example, cerebral endothelial cells secrete MMPs after ischemic injury. These MMPs, in turn, damage the myelin sheath produced by oligodendrocytes. Moreover, under ischemic conditions, trophic support from astrocyte/endothelium to myelinated axons is disturbed by oxidative stress. The reader is encouraged to seek more detailed reviews describing the events in white matter ischemia.43—45,54)