Fig. 4.
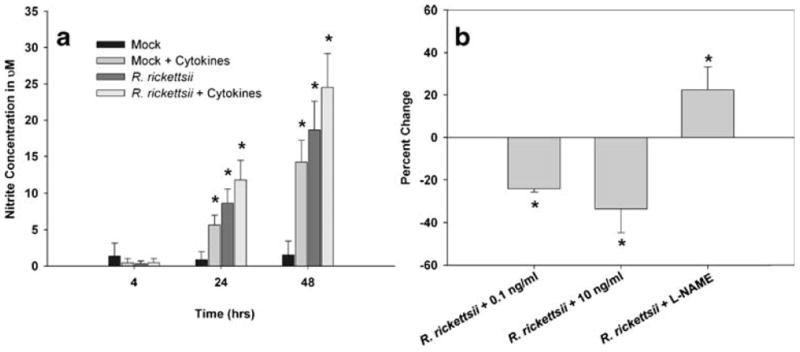
Combinations of pro-inflammatory cytokines induced an increase in microvascular permeability associated with an anti-rickettsial state in endothelial cells. SV-HCEC were infected with 10 MOI of R. rickettsii and/or stimulated with 10 ng/ml of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IFN-γ, and supernatants were collected at the given time points. The concentration of nitrite was determined using the Greiss assay (a). *p<0.05 compared to Mock-treated cells. SV-HCEC were seeded in 24-well plates and grown to confluence at which time they were infected with 10 MOI of R. rickettsii and then stimulated with 0.1 or 10 ng/ml of all three cytokines or treated with 100 uM L-NAME. The percent change in rickettsial genome copies was determined by real-time PCR using the ΔΔCt method with primers to rickettsial gltA and human β-actin (b). *p<0.05 compared to cells only infected with rickettsiae.
