Figure 1.
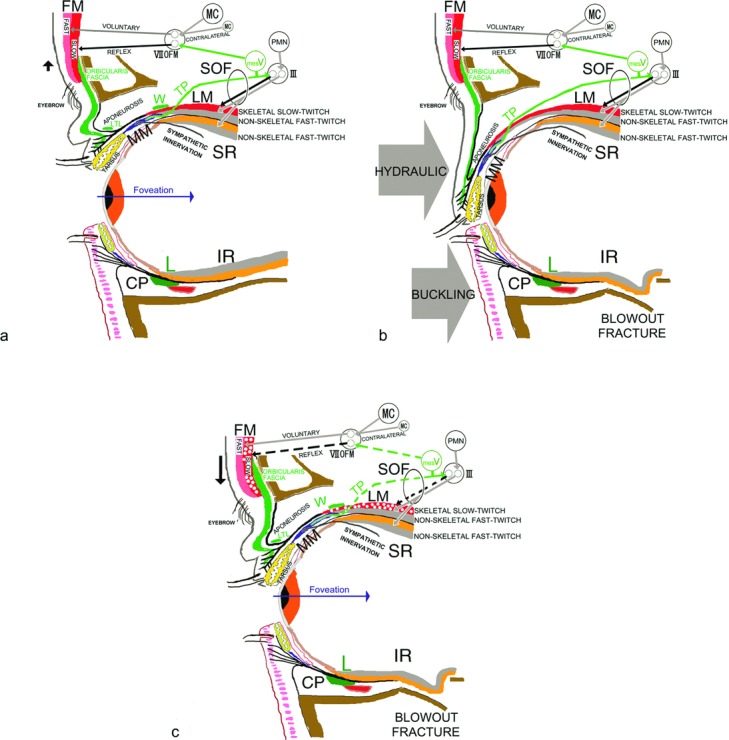
Schematic diagrams of reflex contraction of the levator (LM) and frontalis (FM) skeletal slow-twitch fibers and blowout fracture. (a) Normal eyelid. Voluntary contraction of the frontalis skeletal fast-twitch muscle fibers (Fast) is induced by excitation of the ipsilateral or contralateral motor cortex (MC) and the frontalis subnucleus of the facial nucleus (VIIOFM). Voluntary contraction of the levator (LM) and superior rectus (SR) nonskeletal fast-twitch muscle fibers is induced by excitation of premotor neurons (PMN) and oculomotor neurons (III). Voluntary contraction of the levator and superior rectus nonskeletal fast-twitch muscle fibers stretches the mechanoreceptors in Müller muscle (MM) to evoke trigeminal proprioception (TP), which induces reflex contraction of the levator and frontalis skeletal slow-twitch muscle fibers via the mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus (mesV). (b) Blowout fracture. A hydraulic injury mechanism is induced by a blow force to the globe, whereas a buckling mechanism is caused by a blow force to the orbital rim. (c) After blowout fracture, impairment of trigeminal proprioceptive evocation reduces reflex contraction of the levator and frontalis skeletal slow-twitch muscle fibers, resulting in eyelid and eyebrow ptosis. CP indicates capsulopalpebral fascia; IR, inferior rectus muscle; L, inferior suspensory ligament of Lockwood; LTL, lower-positioned transverse ligament; SOF, superior orbital fissure; W, Whitnall ligament.
