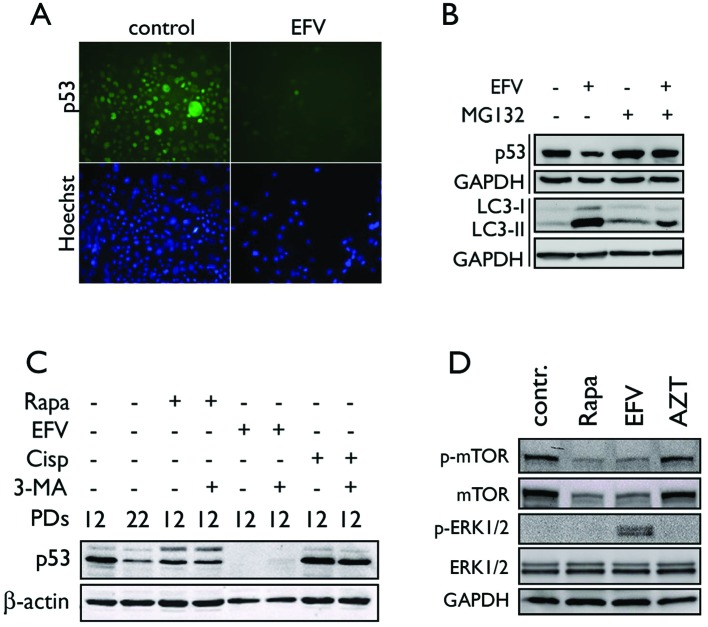
Figure 4.
EFV causes proteosome-dependent degradation of p53. (A) NHKs exposed to 10 μM EFV for 48 h were stained for p53 by indirect immunofluorescence staining and Hoechst 33342 counterstain. Original magnification, ×100. (B) NHKs were exposed to 10 μM EFV for 48 h with or without the addition of 10 μM MG132 2 h prior to collection. Western blotting was performed for p53 and LC3. (C) NHKs at PD 12 were exposed to 10 μM EFV for 48 h, 100 nM rapamycin (Rapa) for 5 days or 10 μM cisplatin (Cisp) for 24 h in the absence and presence of 3-MA (5 mM). The p53 level was determined by western blotting. (D) NHKs were exposed to EFV, rapamycin (Rapa), or AZT, and the cells were assayed for phosphorylated and total mTOR, and phosphorylated and total ERK1/2. β-actin or GAPDH served as a loading control.