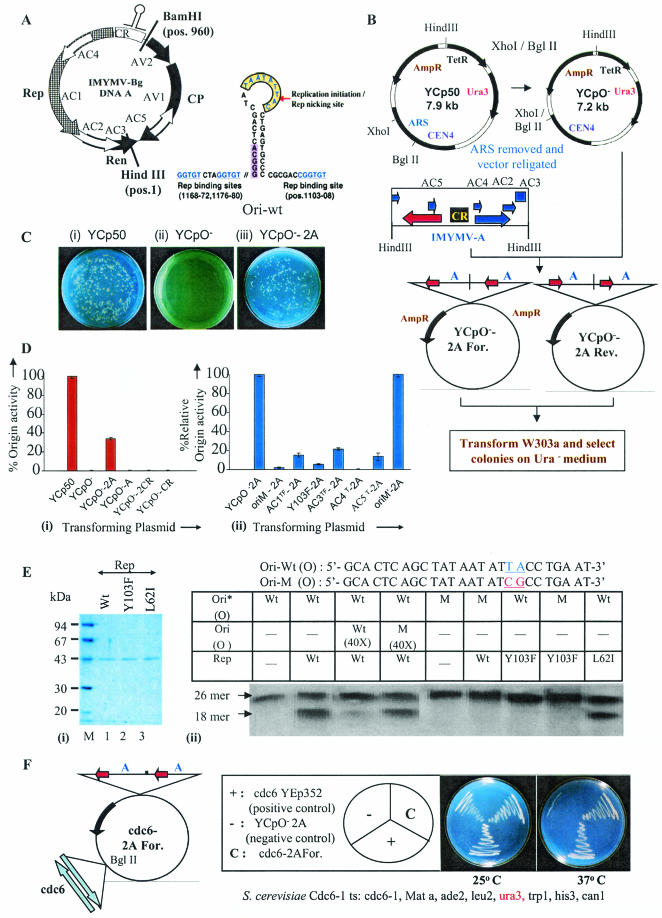
FIG.1.
Genetic studies on geminiviral replication in yeast. (A) Genome organization of IMYMV Black-gram isolate (IMYMV-Bg) DNA-A. An enlargement of the characteristic hairpin loop region containing the conserved nonamer sequence TAA TAT TAC where Rep initiates RCR (Rep cutting site [arrow]) is shown to the right. The various ORFs with their directions of transcription are shown. The putative Rep-binding sites are underlined. The unique sites of BamHI and HindIII are marked. (B) Strategy used to make the replication-competent virus recombinant plasmid YCpO−-2A. The nomenclature YCpO−-2A-For or -Rev was on the basis of orientation of the AV1 ORF with respect to the AmpR gene in YCpO−. (C) Representative plates comparing colonies obtained of the transformed yeast W303a strain (MATa leu2 ura3 his trp1 ade2) with plasmid YCp50 (i), YCpO− (ii), or YCpO−-2A (iii). (D) Panel i, % origin activity of the various constructs relative to YCp50, which was given a value of 100; panel ii, mutation of different ORFs in the DNA-A (in the YCpO−-2A background), namely, AC1, AC3, AC4, and AC5, led to a decrease in origin function (% relative origin activity) compared to plasmid YCpO−-2A, which was given a value of 100 in this case. The superscripts T and TF stand for termination and termination followed by frameshift mutations, respectively. (E) Panel i, SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profile showing the apparent homogeneity in preparations of recombinant Rep and its mutant proteins. AC4T and L62I-Rep represent the same mutant. Panel ii, in vitro site-specific cutting activity of various recombinant versions of Rep with either a wild-type (Ori Wt) or mutant (OriM) oligonucleotide (sequences are indicated at the top). The 43-kDa Rep Wt was able to efficiently cut the 5′-labeled (*) Ori-Wt oligonucleotide (lane 2), and this site-specific nicking was competed out by 40× unlabeled Ori Wt (lane 3), but not by OriM (lane 4). 1× oligonucleotide represents about 1 ng of the 26-mer oligonucleotide. (F) cdc6 complementation. cdc6-YEp352 and YCpO−-2A plasmids were used as a positive and negative control, respectively. The plasmids used for transformation are shown in the sector diagram. All colonies were scored on Ura dropout plates.