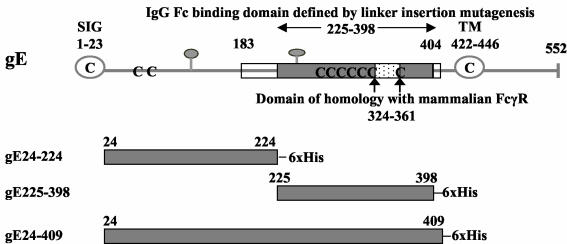
FIG. 2.
Features of HSV-1 gE. Stick diagram of HSV-1 strain NS gE (top) showing the signal peptide (SIG, open circle), transmembrane domain (TM, open circle), potential N-linked glycosylation sites (gray balloons), and cysteine residues (C). The gray shaded box indicates the margins of the IgG Fc binding domain as defined by linker insertion mutagenesis (amino acids 225 to 398), the white boxes show the amino and carboxyl termini outer margins of the IgG Fc binding domain based on studies with gE/gD fusion proteins (amino acids 183 to 404), and the white speckled box marks the domain of homology with mammalian FcγRs (6). The gray shaded boxes (bottom three figures) represent the regions of HSV-1 gE expressed in baculovirus, which include gE protein coding sequences from amino acids 24 to 224 (gE24-224), 225 to 398 (gE225-398), and 24 to 409 (gE24-409). 6× His, six histidine residues added at the carboxyl terminus. The amino acid sequence of the ectodomain of NS gE differs from the published HSV-1 strain 17 gE sequence in that NS gE contains an insertion of two amino acids (Gly and Glu) at positions 186 and 187 (H. M. Friedman, unpublished observation) (27). The numbering system used in the current paper differs from that in our previous publications based on these two added amino acids (1, 6, 30).