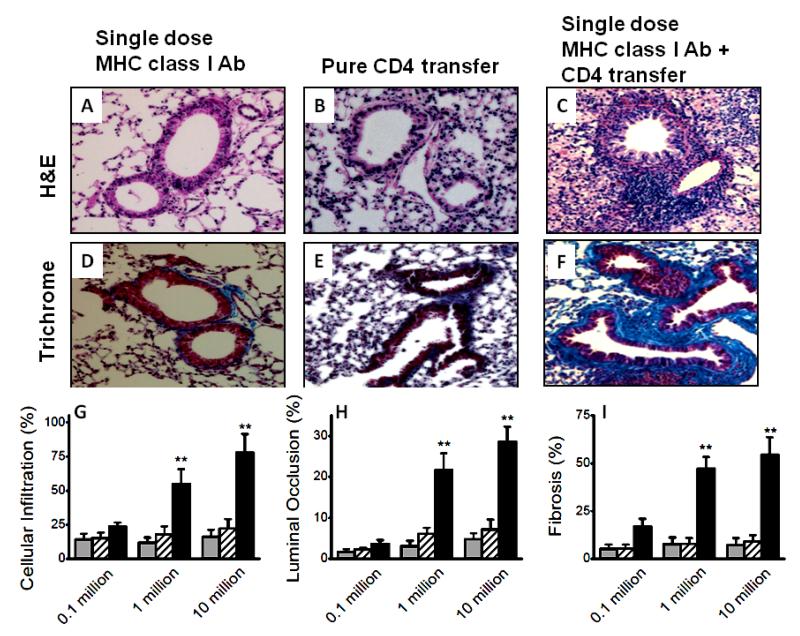
Figure 3.
Induction of OAD by adoptive transfer of CD4+ T cell subsets from LILs of C57BL/6 animals with OAD (following administration of 200 μg of Abs to MHC class I intrabronchially to C57Bl/6 mice on days 1, 2, 3, and 6, and weekly thereafter) into naïve animals with single dose of Abs to MHC class I. Representative H&E stain, (A-C); trichrome stain, (D-F); of the sections taken from day 30, following suboptimal single dose 200 μg MHC class I Abs administration (A and D), pure 10 million CD4+ T cell transfer (B and E) and CD4+ T cell transfer along with suboptimal single dose 200 μg MHC class I Abs administration (C and F). Morphometric analyses on the sections to measure cellular infiltration (G), luminal occlusion (H), and fibrosis (I) from various groups. A dose dependent increase in lesions upon adoptive transfer of 0.1, 1 and 10 million CD4 T cell transfer; suboptimal single dose 200 μg MHC class I Abs administration (grey), pure CD4 T cell transfer (cross-line) and CD4 T cell transfer along with suboptimal single dose 200 μg MHC class I Abs administration (black). Representative of 5 different sections and presented as mean ± SEM. The significance (p-value <0.05) was determined by student t-test; (*) p-value <0.05, statistically significant different between the comparison groups; (#) p-value >0.5, statistically insignificant difference between the comparison groups.