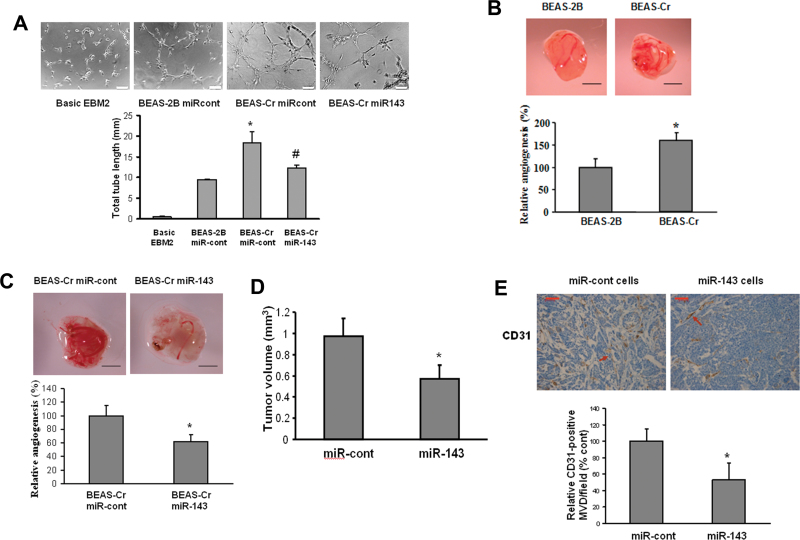
Fig. 2.
Ectopic expression of miR-143 inhibits Cr (VI)–induced tumor angiogenesis. (A) HUVECs were cultured in serum-free medium overnight and resuspended in EBM-2 basic medium. To perform the tube formation assay, HUVECs were incubated in EBM-2 basic medium; conditioned medium prepared from BEAS-2B or BEAS-Cr was transfected with pre–miR control or pre-miR-143, respectively. Tube formation was determined under light microscope after the culture for 12h. Total tube lengths (mm) were presented as mean ± SE from six replicates for each treatment. * and # indicate significant differences compared with BEAS-2B and with BEAS-Cr miR-cont, respectively (p < 0.05). Scale bar: 100 μm. (B and C) BEAS-2B and BEAS-Cr cells were transfected with or without 25nM pre-miR-143 and pre–miR control precursor, respectively. After transfection (24 h), 2 × 106 cells were trypsinized, suspended, and mixed with equal volume of Matrigel and implanted onto the chicken CAMs of 10-day-old chicken embryos. The branches of blood vessels were counted as the relative angiogenesis using 8–10 embryos per treatment 96h after implantation. The data represent as mean ± SE of blood vessel numbers, which were normalized to that of the control. Scale bar: 2 mm. * indicates significant difference compared with that of the control (p < 0.05). (D) Tumor xenograft model in nude mice was established as described in Materials and Methods section. Stable BEAS-Cr cells overexpressing miR-143 or negative miR control were implanted sc into the both flanks of nude mice. Tumor volumes were measured 4 weeks after the cell injection according to the formula (width2 × length)/2 and presented as mean ± SE (n = 10). (E) Mice were euthanized, and tumor sections from the nude mice were used for immunohistochemical staining using antibodies against CD31. Scale bar: 50 μm. Arrow: CD31-positive staining vessels.