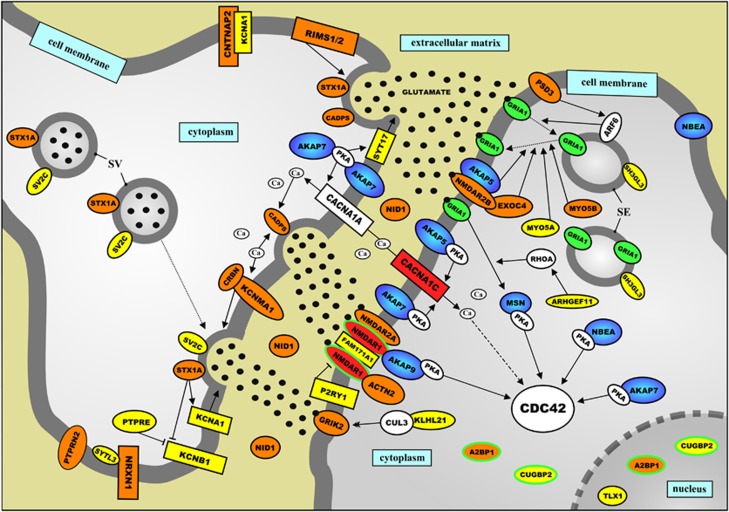
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of a protein network that is located in the neuronal synapse and implicated in autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) by its involvement in modulating glutamatergic neurotransmission. The proteins encoded by genes implicated in ASDs through common genetic variants—single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from five published genome-wide association studies (GWASs) (Supplementary Table 1) and/or ASD candidate gene association studies—are indicated in yellow. The proteins encoded by genes implicated in ASD aetiology through rare genetic variants—one or more mutations and/or copy number variations (CNVs) affecting the gene—are indicated in red, whereas the proteins encoded by genes implicated in ASDs through both common and rare genetic variants are indicated in orange. In addition, all A-kinase anchor proteins (AKAPs) are dark blue and the proteins encoded by genes that have been implicated in ASD aetiology through ‘other' genetic evidence—including gene expression studies, gene/protein function studies and genetic animal studies—are green/have a green border. In the Supplementary Information, the network is described in detail, and the current knowledge about the function of the network proteins is presented.