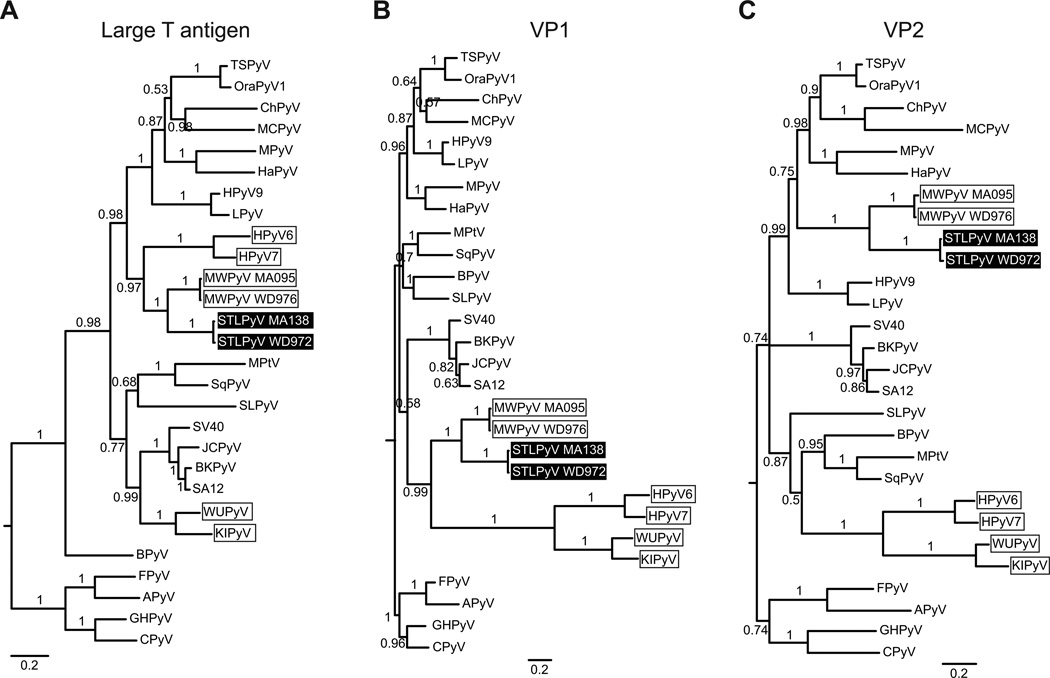
Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of STLPyV.
Phylogenetic relationships of 28 diverse polyomavirus sequences were inferred from alignment of protein sequences from LTAg (A), VP1 (B) and VP2 (C). Avian polyomaviruses were used as an outgroup to root the phylogenies. STLPyV strains are highlighted in black; MWPyV strains and Wukipolyomavirus whose members show discordant phylogenetic relationships are indicated by boxes. Internal branch labels indicate Bayesian posterior probabilities. The ML method yielded trees with similar topologies.