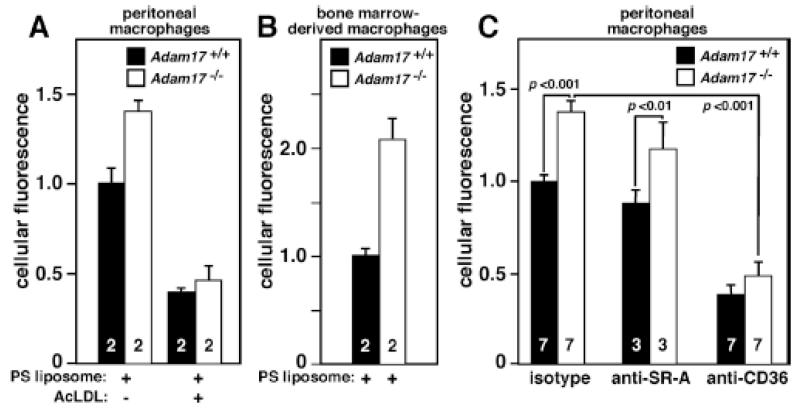
Figure 2. Adam17-null peritoneal and bone marrow-derived macrophages show increased phosphatidylserine liposome binding/uptake, and peritoneal macrophage uptake is CD36-dependent.
A. Peritoneal macrophages from WT or Adam17-null hematopoietic chimera mice were harvested 96 hours after thioglycollate injection, and either plated and treated with or without acetylated-LDL at 4°C for 15 minutes followed by incubation with 40 μmol/L fluorescently labeled phosphatidylserine (PS) liposomes for 4 hours at 4°C. B. Bone-marrow-derived macrophages were isolated from whole bone marrow of WT or Adam17-null hematopoietic chimera mice and cultured for 7 days with M-CSF. Adherent cells were replated, and PS liposome binding was monitored as described in A. C. Peritoneal macrophages were plated and incubated with 160 μmol/L fluorescently labeled PS liposomes and 5 mg/L of either receptor-blocking or isotype control antibody for one hour at 37°C. Fluorescence was assessed by flow cytometry, numbers within the bars indicate the number of mice evaluated, and p values for significant differences are shown.