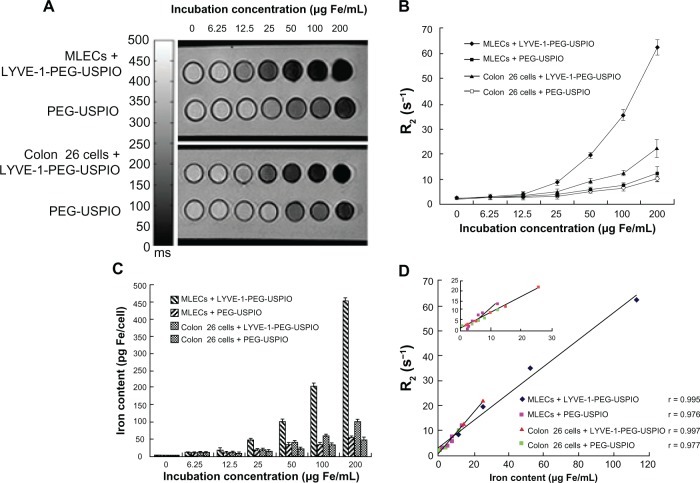
Figure 7.
Notes: (A) T2-weighted MR images of MLECs and colon 26 cells incubated with LYVE-1- PEG-USPIO and PEG-USPIO nanoparticles at different concentrations for 2 hours. (B) Different relaxation rates of MLECs and colon 26 cells incubated with increasing iron concentrations of LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO and PEG-USPIO nanoparticles. The graph indicated the increasing R2 at higher LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO and PEG-USPIO concentrations of MLECs and colon 26 cells. The R2 of LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO labeled MLECs was significantly higher than the other three kinds of labeled cells at iron concentrations of 25 to 200 μg Fe/mL. (C) Iron content (pg Fe/cell) of LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO and PEG-USPIO labeled MLECs and colon 26 cells was determined by AAS after incubation with different concentrations of nanoparticles for 2 hours. Higher cell binding iron content was observed for LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO than PEG-USPIO in two cell lines. Highest binding was found in LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO labeled MLECs. (D) Comparison of MR relaxation rate, R2, and iron content of LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO labeled MLECs, PEG-USPIO labeled MLECs, LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO labeled colon 26 cells, and PEG-USPIO labeled colon 26 cells revealed significantly positive correlations.
Abbreviations: LYVE-1-PEG-USPIO, lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor-1 binding polyethylene glycol-coated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide; MLECs, mouse lymphatic endothelial cells; MR, magnetic resonance; PEG-USPIO, polyethylene glycol-coated ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide.