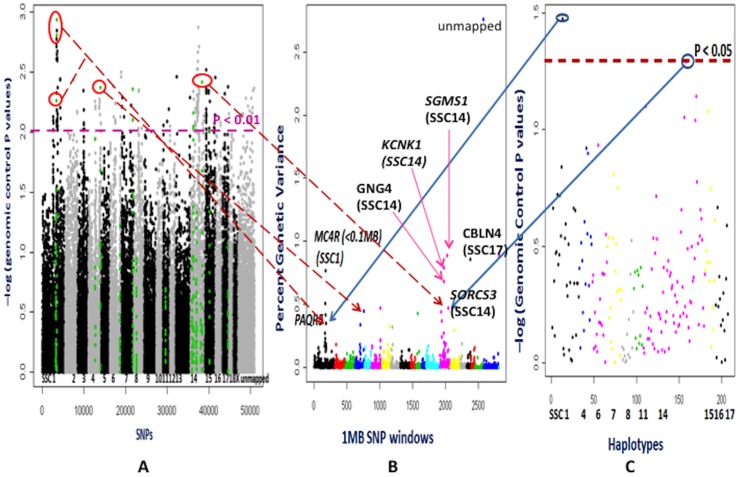
Figure 6. Whole genome association studies for average daily feed intake (ADFI).
Part A depicts association analyses performed by the PLINK software for each SNPs. The X axis shows SNPs across chromosomes 1 to X, unassigned contigs, Y and completely unmapped SNP. The Y axis represents the negative logarithm of the P values corrected for genomic control. Each spot is a SNP. The green color SNPs are those located in 1 Mb window regions that explain more than 0.2% of genetic variance in part B. Part B illustrates results from the Bayes B model averaging approach used in the GenSel software. Different colors on the X axis indicate genome wide 1 Mb SNP windows from chromosome 1 to X, unassigned contigs, Y and completely unmapped SNP. The markers from completely unmapped and unassigned contigs were not included in the cumulative genetic variance. The Y axis represents percent genetic variance explained by each 1 Mb window. Part C shows association analyses with the PLINK software based on haplotypes, which were derived for 1 Mb windows that explained a higher than 0.2% of genetic variance in part B. The X axis depicts chromosomal positions of haplotypes. The Y axis shows the negative logarithm of the P values corrected by genomic control. The arrows in parts A, B and C show the similarities in significant locations of the associated SNPs, SNP windows and their haplotypes. The 1 Mb windows that explained higher than 0.2% percent genetic variance in GenSel analyses and/or were significant in the PLINK analyses were considered to be important putative QTL for ADFI. SGMS1: spingomyelin synthase 1; CBLN4: cerebellin 4; KCNK1: potassium channel, subfamily K, member 1; MC4R: melanocortin 4 receptor; PAQR5: progestin and adipoQ receptor family member V; GNG4: guanine nucleotide binding protein 4; SORCS3: sortilin-related vps10 domain containing receptor 3.