Table 1. The impact of‘respiratory’ variability in intrathoracic pressure and central haemodynamics on cerebral blood flow velocity during the struggle phase.
| Input |

|
|||
 (%) (%) |
Direct | Indirect | Total | |
| ITP | 5.5±0.8 | – | 0.366 | 0.366 |
| HR | 3.3±0.4 | – | 0.219 | 0.219 |
| LVSV | 5.9±0.5 | – | 0.474 | 0.474 |
| CO | 7.6±0.5 | – | 0.536 | 0.536 |
| MAP | 1.8±0.2 | 0.901 | – | 0.901 |
Values represent standardised ß-coefficients obtained from the ‘reduced-fit’ model depicted in
Figure 2
. 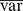 : mean variability (coefficient of variation in percent) observed in the corresponding parameter during the struggle phase of breath holding; ITP: intrathoracic pressure; HR: heart rate; LVSV: left ventricular stroke volume; CO: cardiac output; MAP: mean arterial blood pressure; CBFV: cerebral blood flow velocity. aThe standard deviation of ITP is presented here as a measure of respiratory variability in place of the coefficient of variation (see Methods). The group-average for
: mean variability (coefficient of variation in percent) observed in the corresponding parameter during the struggle phase of breath holding; ITP: intrathoracic pressure; HR: heart rate; LVSV: left ventricular stroke volume; CO: cardiac output; MAP: mean arterial blood pressure; CBFV: cerebral blood flow velocity. aThe standard deviation of ITP is presented here as a measure of respiratory variability in place of the coefficient of variation (see Methods). The group-average for 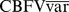 used in the above Path analysis was 2.2±0.1%.
used in the above Path analysis was 2.2±0.1%.
