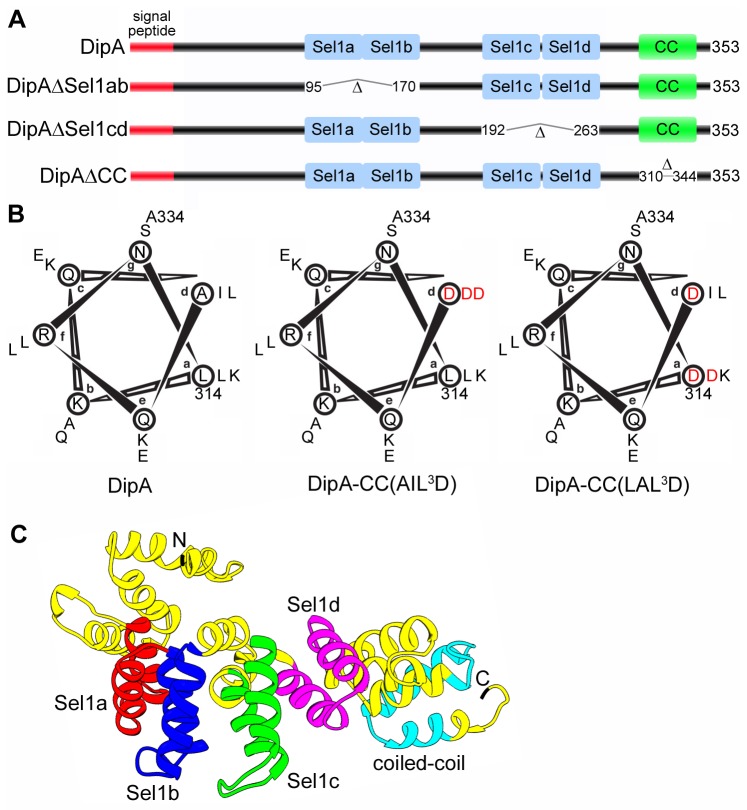
Figure 1. Predicted structure of DipA.
(A) Schematic representations of DipA and domain deletion mutants generated in this study. The predicted N-terminal 20 amino acid signal peptide is denoted is red, the Sel1-like repeat domains are denoted in blue and the coiled-coil (CC) domain is denoted in green. Domain deletion mutants were designed to encompass deletion of Sel1a and Sel1b domains (DipAΔSel1ab), Sel1c and Sel1d domains (DipAΔSel1cd), and the CC domain (DipAΔCC). (B) Helical wheel representations of the CC domain corresponding to amino acid residues of DipA. Heptad-repeat positions are denoted a to g. Two DipA CC domain substitution mutants where three hydrophobic residues in core positions a and d were mutated to aspartate [DipACC(AIL 3D) and DipACC(LAL 3D)]. Mutations are indicated in red. (C) Three-dimensional ribbon model of DipA predicted by I-TASSER and visualized using Chimera software. The Sel1a domain corresponding to residues 96-132 is indicated in red, the Sel1b domain corresponding to residues 133-169 is indicated in blue, the Sel1c domain corresponding to residues 193-229 is indicated in green, the Sel1d domain corresponding to residues 231-262 is indicated in purple, and the CC domain corresponding to residues 311-343 is indicated in cyan.