Figure 2. DipA is a surface-exposed, membrane-associated protein.
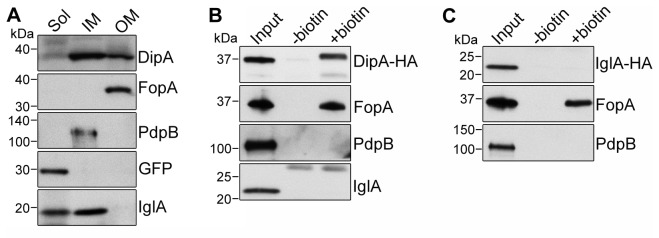
(A) Subcellular localization of DipA, FopA, PdpB, GFP, and IglA from GFP-expressing SchuS4. Soluble (Sol), inner membrane (IM), and outer membrane (OM) enriched fractions were separated based on Sarkosyl solubility and subjected to immunoblot analysis with antibodies against DipA, FopA, PdpB, GFP and IglA. Each fraction was concentrated to the same volume and equal volumes were loaded. GFP, PdpB and FopA were used as soluble, inner membrane and outer membrane markers, respectively. (B and C) Immunoblot analysis of purified surface biotinylated proteins from SchuS4ΔdipA(pdipA-HA) (B) or SchuS4(piglA-HA) (C) lysates. DipA-HA and IglA-HA were detected using anti-HA antibodies. FopA was used as a positive control; PdpB and IglA were used as negative controls. Input, untreated (-biotin) and biotinylated (+biotin) samples were processed for CFU enumeration and immunoblotting as described in Materials and Methods. Samples were loaded based on CFU equivalents as follows: 1x107 (Input) or 1x108 (-/+ biotin) for anti-DipA-HA analysis, 5x106 (Input) or 1x108 (-/+ biotin) for anti-FopA analysis, 1x107 (Input) or 5x108 (-/+ biotin) for anti-PdpB analysis, 1x107 (Input) or 5x108 (-/+ biotin) for anti-IglA analysis, 1x107 (Input) or 5x108 (-/+ biotin) for anti-IglA-HA analysis.
