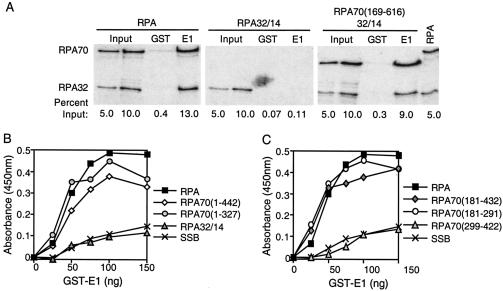
FIG. 2.
E1 interacts with DBD-A of RPA's major ssDNA-binding domain. (A) Bacterially expressed GST or GST-E1 proteins were purified on glutathione Sepharose beads. These beads were incubated with 0.8 to 1.0 μCi of radiolabeled full-length or truncated RPA proteins in the presence of micrococcal nuclease for 3 h at 4°C. The beads were precipitated by centrifugation, washed, and subjected to SDS-PAGE. RPA retained by the beads was visualized by phosphorimager analysis, and the intensity of the bands was quantitated using Quantity One software. Each assay was repeated at least three times. The results depicted were taken from a representative experiment. The lanes marked “Input” consist of 5 or 10% of radiolabeled RPA used in each precipitation that was directly subjected to SDS-PAGE without precipitation. The lanes marked “GST” contain proteins precipitated using GST-bound glutathione Sepharose beads. The lanes marked “E1” contain proteins precipitated using GST-E1-coated glutathione Sepharose beads. The lane marked “RPA” contains the radiolabeled full-length RPA, which was directly subjected to SDS-PAGE. The 70- and 32-kDa subunits of full-length RPA are labeled RPA70 and RPA32, respectively. Due to its small size and low level of labeling, RPA14 is not shown. The percentages on the bottom of each figure are the percent radioactive RPA that was loaded or precipitated in that lane compared to the total RPA added to each reaction mixture. (B) Full-length RPA, RPA mutants with truncations of the RPA70 carboxyl terminus, RPA32/14, and SSB were tested for their ability to bind to BPV1 E1 in ELISA-based protein interaction assays. The carboxyl terminus of RPA70 was truncated up to amino acid residues 442 and 327 in the RPA mutants RPA70(1-442) and RPA70(1-327), respectively. These mutants were expressed without RPA32 or RPA14. The proteins were immobilized in ELISA wells in equimolar amounts (4 pmol). The wells were blocked and then challenged with increasing concentrations of GST-E1. The wells were washed, and the retained GST-E1 was measured as described in Materials and Methods. (C) Full-length RPA; RPA mutants consisting of the major ssDNA-binding domain of RPA [RPA70(181-432)], DBD-A [RPA70(181-291)], or DBD-B [RPA70(299-422)]; and SSB were also tested for their ability to bind to BPV1 E1 in ELISA-based protein interaction assays. Four picomoles of each protein was immobilized in ELISA plate wells. The wells were blocked and then challenged with increasing concentrations of GST-E1. The wells were washed, and the retained GST-E1 protein was detected as described above. Each of these assays was performed at least three times. Panels B and C each depict data from a representative experiment.