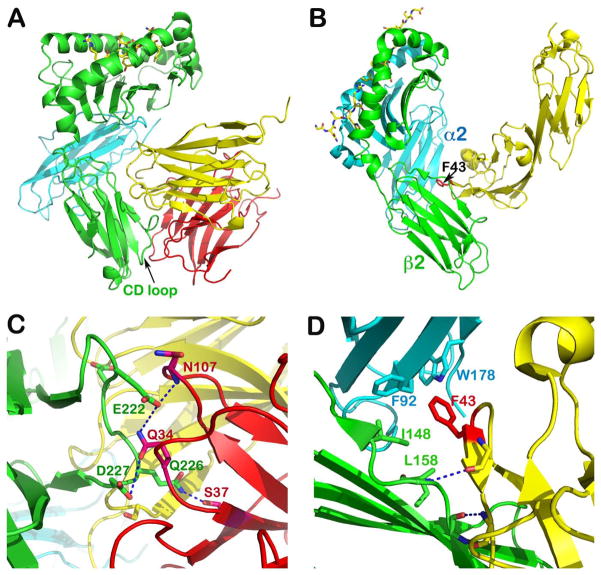
Fig. 11. Structure of TCR co-receptors.
(A) Crystal structure of murine H2-Kb in complex with CD8αα homodimer (PDB 1BQH). For the H2-Kb, the heavy chain is in green and β2 microglobulin is in cyan, whereas the two subunits of CD8αα are in yellow and pink, respectively. The peptide is shown as a stick model within the groove. Note that the CD loop of H2-Kb is clamped by CDR loops of CD8αα homodimer. (B) Crystal structure of murine I-Ak in complex with the N-terminal two domains of CD4 (PDB 1JL4). The α and β subunits of I-Ak are in cyan and green, respectively, whereas the CD4 is in yellow. The peptide is in stick model representation lying in the groove. Note how the CD4 domain 1 wedges between α2 and β2 domain of I-Ak with hotspot residue, F43 poking into the MHCII hydrophobic pocket. (C) Specific interaction between CD8αα and H2-Kb’s CD loop. Conserved residues involved in these hydrogen bondings are labeled. (D) Specific interaction between CD4 and I-Ak. The two main chain hydrogen bonds between the edge β strands of CD4 and β2 domain of I-Ak docks the CD4 onto I-Ak. This brings F43 of CD4 into hydrophobic pocket formed between α2 and β2 domains whose key contacts are shown.