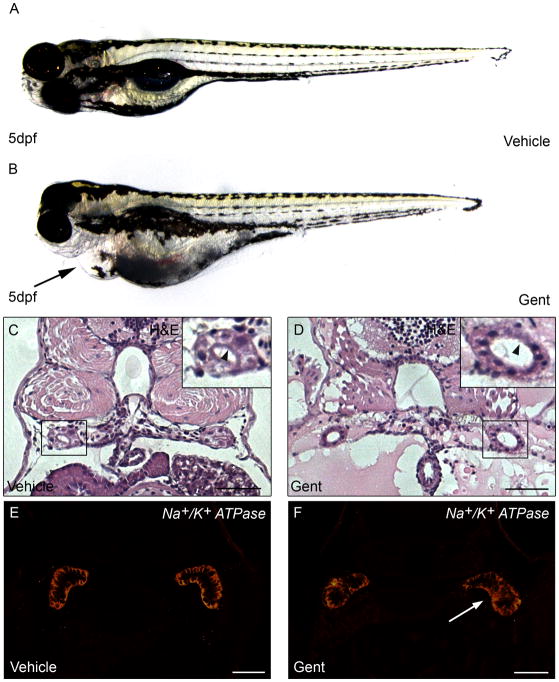
Figure 1. Gentamicin-mediated AKI in zebrafish.
(A,B) Zebrafish larvae at 5 days post fertilization (dpf) injected with (A) vehicle or (B) 7.5 ng gentamicin. Arrow indicates pericardial edema reflecting kidney damage. (C–D) Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of kidney sections 72 hours post-treatment in (C) vehicle and (D) gentamicin-injected larvae. Inset shows the pronephric tubules, with tubular distension and loss of brush border (compare D with C, arrowheads). (E–F) Immunofluorescence for Na+/K+ATPase 48 hours post-treatment in (E) vehicle and (F) gentamicin-injected larvae. White arrowhead (F) indicates loss of basolateral polarity in proximal tubules. Scale bar is 20 μm.