Figure 1.
A Computational Model of Protein Translation
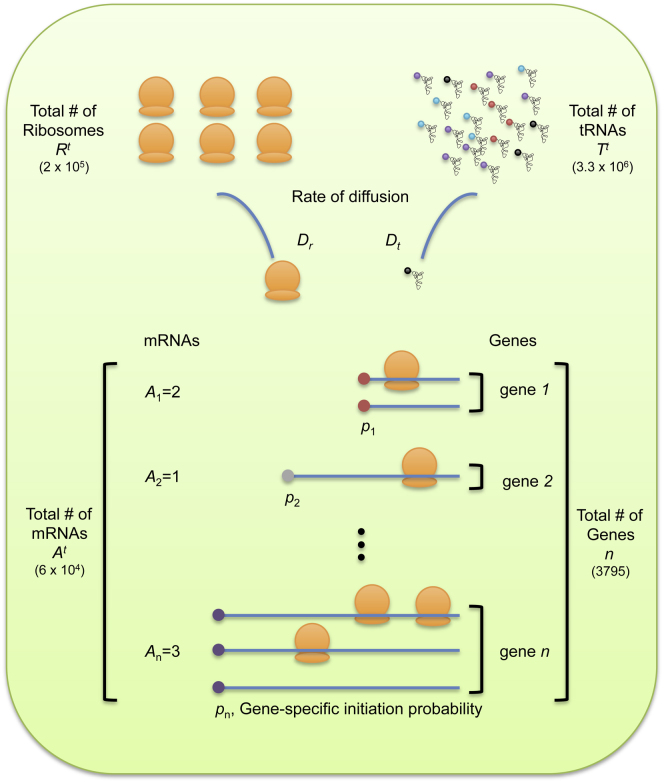
The model tracks the status of all ribosomes, tRNAs, and mRNAs in a cell in continuous time. At any time point, each tRNA and ribosome molecule is either diffusing freely in the cell or is bound to a specific mRNA molecule at a specific codon position. Translation initiation occurs when a free ribosome diffuses to an mRNA and subsequently, with an mRNA-dependent probability, scans to its start codon. The rate of elongation of each subsequent codon depends on the abundance of free cognate tRNAs and their diffusion to the bound ribosome. All rates are based on experimentally determined parameters, including the cell volume, numbers of mRNAs, total abundances of ribosomes and tRNAs, and their diffusion constants. A precise definition of the Markov state space, illustrative pseudocode, and the complete source code for simulation are provided in the Supplemental Information. See also Figure S1, Tables S1 and S2, and Data S1 and S2.