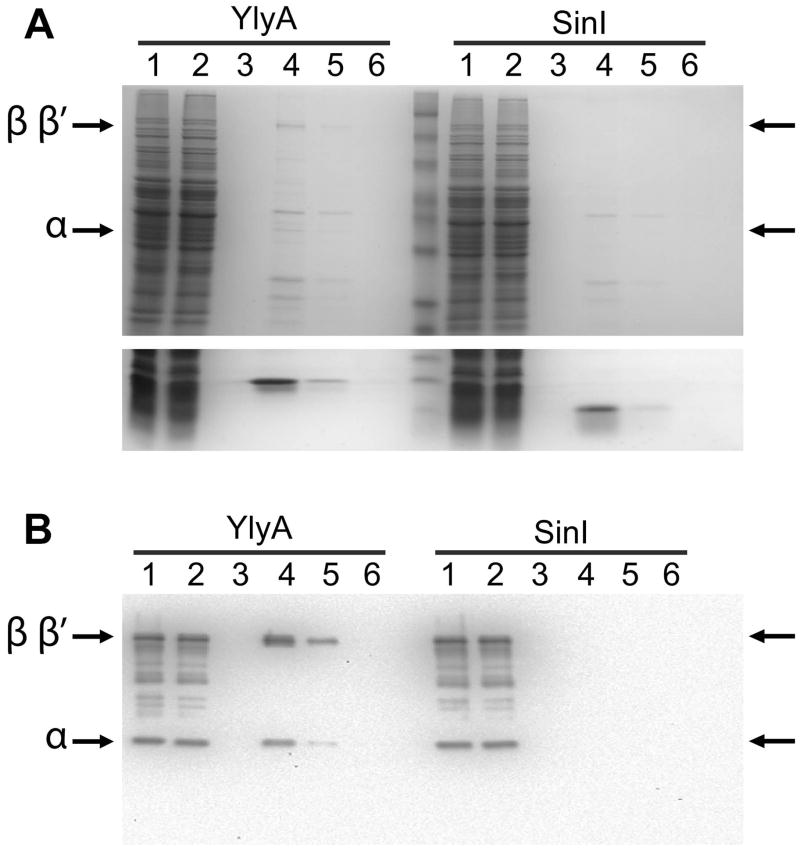
Fig. 5. YlyA interacts with RNA polymerase from a lysate.
Recombinant hexahistidine-tagged YlyA or SinI was passed over a metal affinity resin. Next a soluble protein lysate from sporulating cells of a ylyA mutant was applied to the column. The column was washed and then eluted with imidazole. Lanes: soluble protein lysate (1), flow through (2), wash (3), elution fractions (4–6). (A) Top panel: 10% SDS/PAGE gel showing bands corresponding to the β/β′ and αsubunits of RNA polymerase (indicated by arrows) which co-eluted with YlyA (left half of the gel) but not SinI (right half of the gel); Bottom panel: 15% SDS/PAGE gel showing the bands for YlyA (left) and SinI (right) eluted from the column. (B) Western blot analysis. Bands were transferred to a membrane, and the membrane was probed with antibodies raised against purified Bacillus RNA polymerase. Arrows indicate bands corresponding to the β/β′ and α subunits of RNA polymerase which co-eluted with YlyA (left half of the gel) but not SinI (right half of the gel).