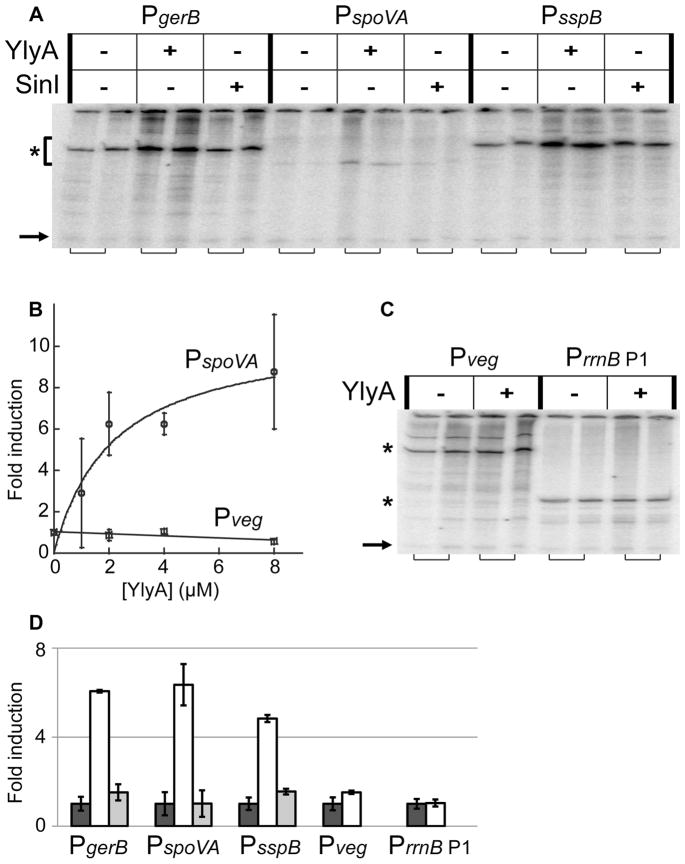
Fig. 6. YlyA stimulates σG-dependent, but not σA-dependent, promoters in vitro.
Multiple round in vitro transcription assays using 10 nM purified B. subtilis RNA polymerase, recombinant sigma factors, and hexahistidine-tagged YlyA or SinI. (A) Experiments with purified σG and plasmid templates carrying the σG-dependent PgerB, PspoVA or PsspB promoters, showing stimulation by YlyA. Dilution buffer, 8 μM YlyA, or 8 μM SinI were included in the reactions. Specific signals are indicated by an asterisk to the left of the gel. Adjacent lanes (indicated by brackets below the gel) are from duplicate reactions. Arrow to the bottom left of the gel indicates the end-labeled probe included during phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation (see Experimental Procedures). (B) The effect of YlyA on transcription with σG-dependent PspoVA is dose-dependent. Transcription with σA-dependent Pveg is unaffected by YlyA. Results are averages from three separate experiments. Error bars indicate standard errors (SEM). (C) Experiments with purified σA and plasmid templates carrying the σA-dependent Pveg or PrrnB P1 promoters, showing these promoters are unaffected by YlyA. Dilution buffer, 8 μM YlyA, or 8 μM SinI were included in the reactions. Specific signals are indicated by asterisks to the left of the gel. Adjacent lanes (indicated by brackets below the gel) are from duplicate reactions. Arrow to the left of the gel indicates end-labeled probe included during phenol/chloroform extraction and ethanol precipitation. (D) Quantification of the specific signals from gels from (A) and (B). Values are averages from the two duplicate experiments. Average signal from the lanes without YlyA or SinI added were set to one, and fold induction with protein added is given relative to that. Error bars indicate standard errors (SEM).