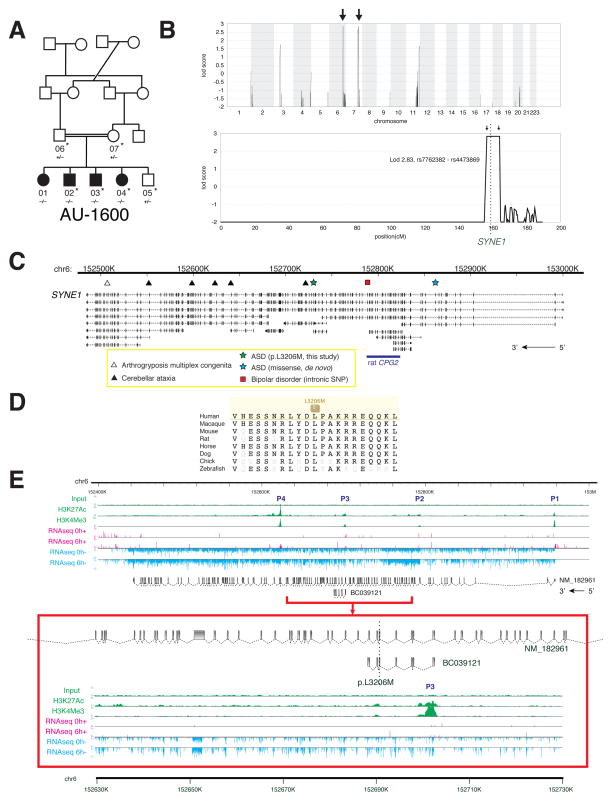
Figure 3.
Identification of mutations in SYNE1 in a family with ASD. (A) AU-1600, a family with four children affected with ASD. Shaded symbols indicate affected individuals. WES was performed on samples from individuals indicated with a star. Genotyping by Sanger sequencing in additional family members was performed where indicated (+: reference allele, −: alternate allele). (B) Mapping rules out the majority of the genome and points out to only two candidate loci, one on chromosome 6 and the other on chromosome 7. Genome-wide linkage plot (top) and maximum obtainable LOD score in the family across the interval (bottom). (C) SYNE1 is a complex locus implicated in neuropsychiatric disease. SYNE1 encompasses multiple alternative transcripts (Known Genes, UCSC Genome Browser), and mutations have been associated with a wide range of neurodevelopmental phenotypes. The location of the recessively inherited missense change in this study is denoted by the green star. Late truncation (open triangle) causes autosomal recessive arthrogyroposis multiplex congenita (Attali et al., 2009), while truncating mutations further upstream (closed triangles) cause autosomal recessive cerebellar ataxia (Gros-Louis et al., 2007). An intronic SNP (red square) is a putative bipolar disorder susceptibility locus (Sklar et al., 2011). A de novo missense change was previously reported in ASD (blue star) (O’Roak et al., 2011). (D) The homozygous missense mutation p.L3206M disrupts a highly conserved residue. (E) Human neuronal ChIPseq and RNAseq data demonstrate transcriptional complexity and activity-dependent regulation of the SYNE1 locus. ChIPseq with antibodies to H3K4Me3 (active promoters) and H3K27Ac (enhancers) demonstrates at least four active promoters (P1–P4) for SYNE1. P3 lies immediately upstream of the residue mutated in AU-1600 (p.L3206M) and corresponds to the active promoter site for BC039121. RNAseq of cultured human neurons was performed before (0h; 0 hours) and after (6h; 6 hours) depolarization with KCl. Depolarization induces upregulation of full-length SYNE1 and the BC039121 isoform compared to untreated neurons (also see Figure S3). The experiment was performed on five biological replicates. Representative tracks are shown. The red square represents a magnification of the region around BC039121. Sense (+; pink) and antisense (−; blue) transcripts are indicated.