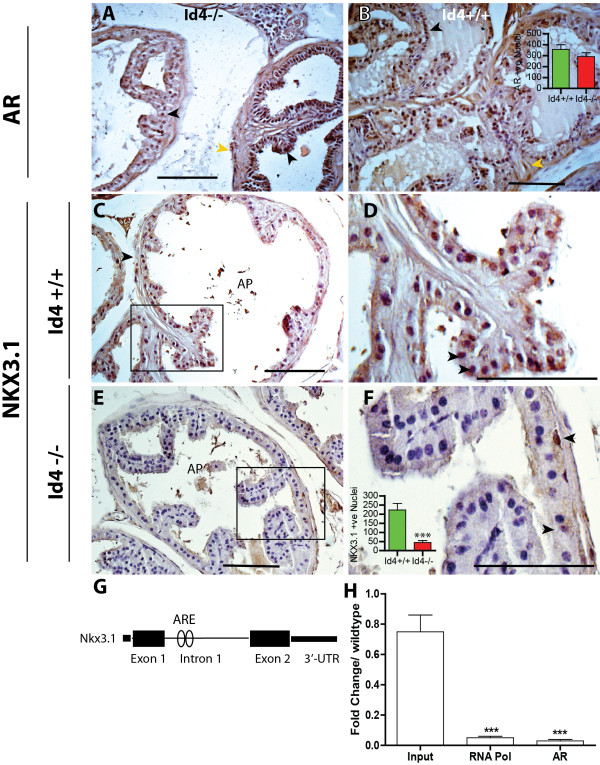
Figure 3.
Loss of Id4 has no effect of Androgen receptor but attenuates NKX3.1 expression. Androgen Receptor (Panels A and B) and NKX3.1 expression (Panels C-F) in wild type (Id4+/+, B, C and D) and Id4 knockout (Id4-/- A, E and F) mice. Androgen receptor (AR) expression was observed in the nucleus (black arrowheads) of both Id4-/- (A) and Id4+/+ (B) prostate epithelial cells. AR was also observed in the stromal cells (yellow arrowheads) in Id4-/- and Id4+/+ mice. Panels C and D: Nkx3.1 is highly expressed in the nucleus of wild type prostatic glandular epithelium cells (black arrowheads, Panel D). Panel D is the enlarged boxed region in Panel C. Panel E: Nkx3.1 expression is undetectable in mice lacking Id4 (Id4-/-), however at higher magnification (Panel F, enlarged boxed region of Panel E) some cells stain positive for Nkx3.1 expression (black arrowheads). The brown staining represents the expression of AR in A and B and NKX3.1 in C-F. Representative images are shown. The AR and Nkx3.1 positive cells were counted in 25 tubules each in Id4+/+ and Id4-/- cross sections. The average AR or Nkx3.1 positive cells per tubule is shown in Panels B and F respectively (***: P < 0.001, t-test, n = 25 tubules). The scale bar is 100um. G: Schematic of Nkx3.1 gene including intron 1. The androgen response element (ARE) in intron 1 binds androgen receptor and regulates androgen dependent expression of Nkx3.1 in mice prostate. H: Chromatin immuno-precipitation (ChIP) based analysis of androgen receptor binding to the ARE site in intron 1 of Nkx3.1. The binding of RNA polymerase I (RNA Pol) and AR was quantitated using real time PCR. The data normalized to IgG shows the input, RNA pol and AR in the Id4-/- knockout prostate as compared to wild type set to 1. (*** P < 0.001, n = 3 in triplicate).