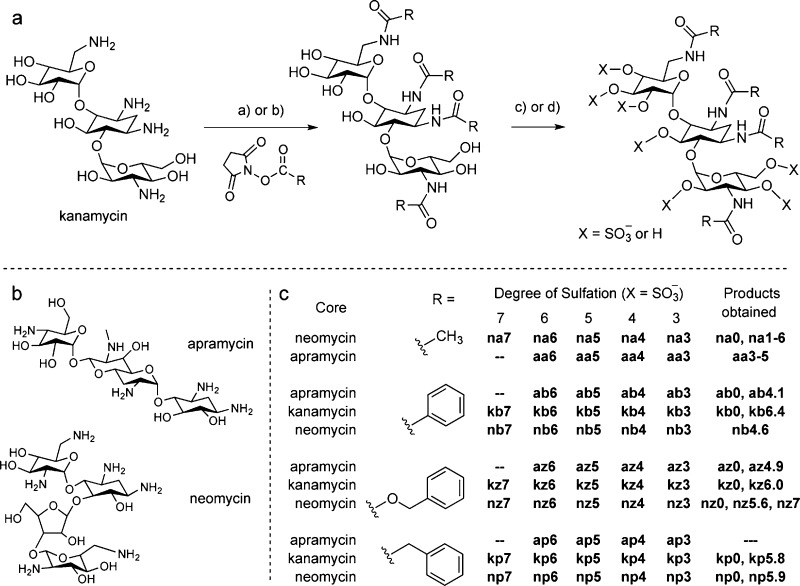
Scheme 1. Synthesis of N-Arylacylated O-Sulfonated Aminoglycosides.
(Panel A) Methods used for the per N-acylation and O-sulfonation of aminoglycosides (kanamycin shown as example). (a) NHS ester, NaHCO3, H2O, 23 °C, 12-16 h, 30-85%; (b) acyl chloride, NaHCO3, H2O; (c) i: Pyr·SO3, DMF, anhydrous pyr, 66 °C, 5-7 h; ii: H2O, 10 mM NaOH, 4 °C, 45-65%; (d) i: ClSO3H, pyr, 57 °C, 4-6 h; ii: H2O, NaHCO3, 35-95%. (Panel B) Structures of apramycin and neomycin. (Panel C) The O-sulfonation reactions give individual products having varied degrees of sulfation. For each aminoglycoside, final products obtained are noted by the core aminoglycoside (n, neomycin; k, kanamycin; a, apramycin), the N-arylacyl group (a, acetyl; b, benzoyl; z, benzyloxycarbonyl; p, phenylacetyl), and the calculated average number of sulfate groups per product obtained (e.g., nz5.6) or range of sulfate groups for the acetyl derivatives (e.g., aa3-5).