Table 1.
Classification features
| Group | Feature | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | m | Number of compounds connected to >2 reactions. |
| u | Number of unpaired compounds. | |
| t | Reaction type: 1—unpaired compounds on both sides of the reaction, 2—unpaired compounds on only one side, 3—no unpaired compounds. | |
| h | Number of chokepoint compounds. | |
| c | Number of compounds. | |
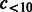 |
Number of compounds connected to >2 and <10 reactions. | |
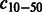 |
Number of compounds connected to 10–50 reactions | |
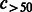 |
Number of compounds connected to >50 reactions. | |
| R | Number of other reactions sharing a compound with this reaction. | |
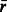 |
Mean number of other reactions connected to each compound. | |
| r1 | Number of connections of the least connected compound. | |
| r2 | Number of connections of the second least connected compound. | |
| r3 | Number of connections of the third least connected compound. | |
| r4 | Number of connections of the fourth least connected compound. | |
| 2 | e | Eccentricity using unweighted edges, |
 |
Normalized eccentricity using unweighted edges. | |
| ew | Eccentricity using weighted edges | |
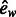 |
Normalized eccentricity using weighted edges | |
| b | Betweenness using unweighted edges | |
| bw | Betweenness using weighted edges | |
| N | Number of reactions in the connected component. | |
| 3 | 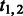 |
Fraction of reactions of type 1 or 2 in the network. |
| 4 | G | Domain: 1—Bacteria, 2—Eukaryota, 3—Archaea. |
| D | 1—species is related to disease, 0—species is not related to disease. |
Note: The features chosen were divided into four groups as shown: 1—local, 2—semi-local, 3—global and 4—non-topological.
