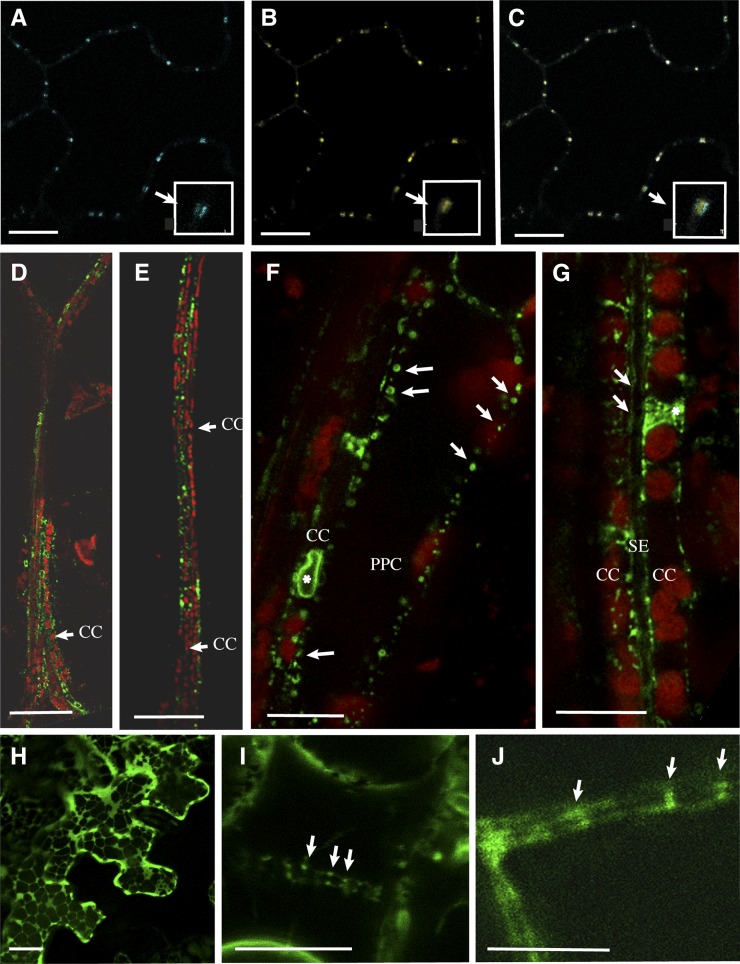
Figure 9.
Localization of NHL26 in Phloem Cells.
Confocal microscopy of NHL26-CFP and NHL26-GFP. PPC, phloem parenchyma cells. Bars = 10 µm in (A) to (C), (F), and (G), 50 µm in (D) and (F).
(A) to (C) Colocalization of NHL26-CFP with PD-associated PDLP1-GFP, observed by confocal microscopy, after the agroinfiltration of pNHL:NHL-CFP into epidermal cells of the cotyledons of p35S:PDLP1-GFP-expressing Arabidopsis plants. PDLP1-GFP signal (A), NHL-CFP signal (B), and overlay of (A) and (B) in (C).
(D) and (E) Localization of the NHL26-GFP fusion protein, in the secondary (D) and minor (E) leaf veins of pNHL:NHL-GFP Arabidopsis plants.
(F) to (G) Subcellular localization of the NHL26-GFP fusion protein in phloem cells in pNHL:NHL-GFP Arabidopsis plants.
(F) Details of subcellular localization in phloem parenchyma and CCs.
(G) Details of subcellular localization in CCs and SEs. In these images, the CCs can be identified by the alignments of chloroplasts, typical of the organization of plastids in these cells. The SEs can be identified by the absence of plastids and the double membrane. Arrows indicate GFP-labeled punctate structures stacked at the periphery of CCs and SEs. Stars indicate a thin network surrounding the nucleus, indicative of a location within the ER.(H) Transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells using the p35S:NHL-GFP construct. (I) Stable expression in Arabidopsis epidermal cells of p35S:NHL-GFP after plasmolysis treatment. (J) Stable expression in vascular cells in pNHL:NHL-GFP Arabidopsis plants. (I) shows, after plasmolysis, punctate structures on both sides of the cell walls in p35S:NHL-GFP, as observed in pNHL:NHL-GFP plants (J), without any plasmolysis treatment. CC, companion cells, SE, sieve elements, PPC, phloem parenchyma cells. Bars = 10 μm in A, B, C, F, H, I, J and G, 50 μm in D and F.