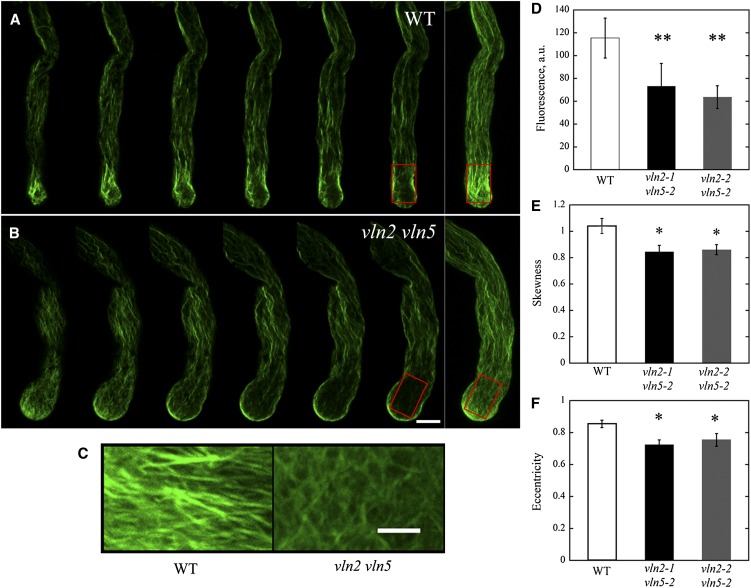
Figure 4.
Actin Collars Do Not Form Properly in vln2 vln5 Pollen Tubes.
(A) Actin filaments in a wild-type (WT) pollen tube. Selected optical sections and a projection (far right panel) are shown. The red box marks the region containing actin structures corresponding to actin collars.
(B) Actin filaments in a vln2-2 vln5-2 pollen tube. Selected optical sections and a projection (far right panel) are shown. Bar = 5 μm for images in (A) and (B). The red box marks the region containing actin structures corresponding to actin collars.
(C) Enlarged images of actin filaments from the boxed regions of (A) and (B). Bar = 2 μm.
(D) The average fluorescence pixel intensity in arbitrary units (a.u.) associated with actin staining decreased significantly in vln2 vln5 pollen tubes. **P < 0.01 by a Student’s t test.
(E) The skewness decreased significantly in vln2 vln5 pollen tubes. *P < 0.05 by a Student’s t test.
(F) The eccentricity of actin filaments in the subapical region of vln2 vln5 pollen tubes decreased significantly, suggesting that the orientation of actin filaments was more irregular in the subapical region of vln2 vln5 pollen tubes. *P < 0.05 by a Student’s t test.