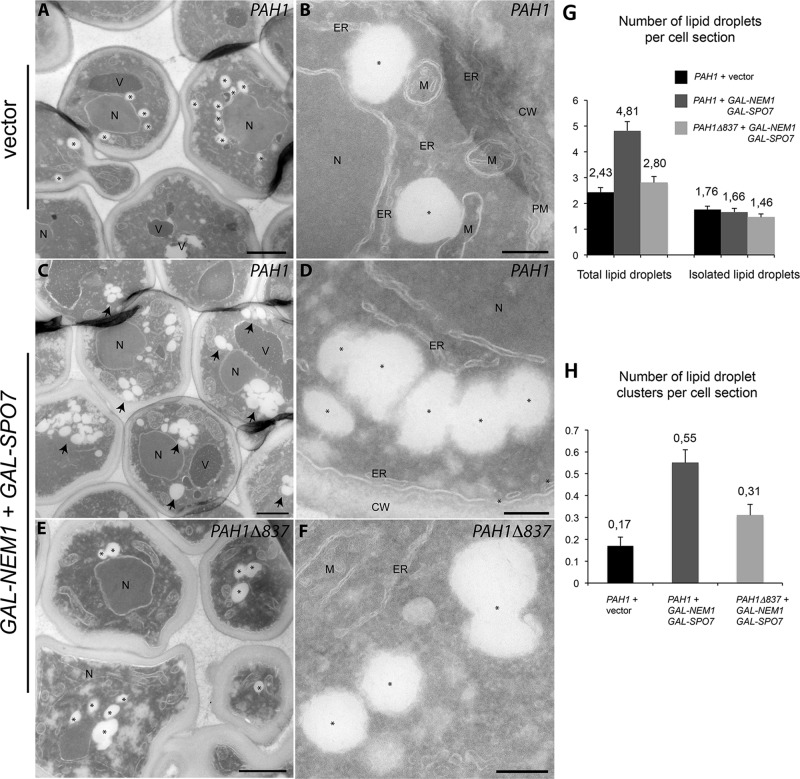
FIGURE 5:
Pah1p acidic tail–dependent formation of lipid droplet clusters. (A–F) pah1Δ cells expressing either PAH1 and vector controls (A, B), PAH1 and GAL-NEM1/GAL-SPO7 (C, D), or PAH1Δ837 and GAL-NEM1/GAL-SPO7 (E, F) were grown in a galactose-containing medium for 5 h as in Figure 4C. Cells were then processed for electron microscopy as described in Materials and Methods. Cryosections were picked up with 0.47% uranyl acetate (mild uranyl pickup) before being immediately stained and viewed with an electron microscope. CW, cell wall; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; M, mitochondria; N, nucleus; PM, plasma membrane; V, vacuole. Lipid droplets are marked with an asterisk (A, B, D–F) or, when in clusters, an arrow. Bars, 1 μm (A, C, E), 0.2 μm (B, D, F). (G) Number of total lipid droplets increases upon induction of Nem1p and Spo7p overexpression in a Pah1p-acidic tail–dependent manner. The total number of lipid droplets (left) or only isolated lipid droplets (right) per cell section was determined over 200 cell profiles randomly selected. (H) The number of lipid droplet clusters (more than three adjacent lipid droplets) per cell section increases when Nem1p and Spo7p are overexpressed in the presence of full-length Pah1p and is partly dependent on the acidic tail. Values represent the mean ± SEM of measurements from at least three different grids.