Figure 1. Selected mAbs against BP-2a 515 variant recognize only the polymerized pilus structures of the homologous strain and can mediate complement-dependent bacterial clearance.
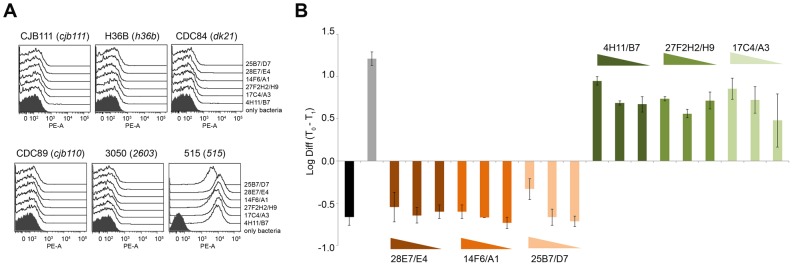
(A) Flow cytometry analysis on whole GBS strains stained with mAbs raised against BP-2a 515 variant. Six GBS strains expressing different BP-2a variants were used in the assay, strain CJB111 (cjb111 allele); strain H36B (h36b allele); strain CDC84 (dk21 allele); strain CDC89 (cjb110 allele); strain 3050 (2603 allele) and strain 515 (515 allele). Fixed bacteria were stained with monoclonal antibodies and then labeled with R-Phycoerythrin conjugated goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies. Black filled histograms indicate staining of bacteria with only secondary antibody. (B) Opsonophagocytosis activity of the selected six monoclonal antibodies. 104 CFUs of GBS strain 515 were incubated for 1 h with differentiated HL60 cells, baby rabbit complement and monoclonal antibody (1∶30, 1∶90, and 1∶270 dilutions). The log10 differences between GBS colony-forming units at time 0 (104 CFU) and time 1 h are shown. The mAbs used are recorded above each bar. Black shaded bars represent negative control (without baby rabbit complement); grey bars correspond to the polyclonal serum specific for the full length BP-2a 515 protein, used as positive control. Error bars indicate standard deviation from two independent experiments.
