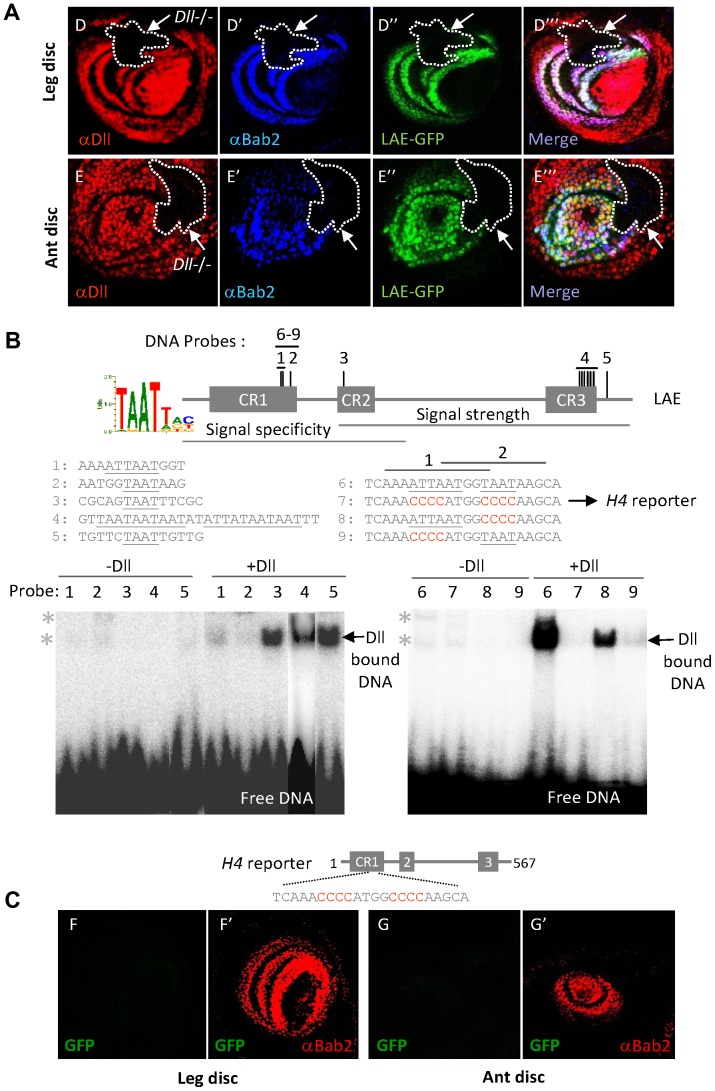
Figure 5. The Dll homeodomain protein positively regulates LAE activity through direct binding to CR1 sequences.
(A) Dll activity is critically required for both bab2 and LAE-GFP expression in developing limbs. Dll immunostaining (red), Bab2 immunostaining (blue) or GFP expression (green) alone, as well as the corresponding merged images, of leg (D–D″′) and antennal (ant) (E–E″′) imaginal discs from late third-instar larvae carrying Dll null mutant clones, are shown. Large DllSA1 mutant clones (circled by dashed white lines) are indicated by white arrows in all panels. Expression of both endogenous bab2 and LAE-GFP reporter was cell-autonomously extinguished in the Dll mutant cells. (B) Dll binds in-vitro to HD-binding motifs located throughout the LAE sequence. The extents of the signal specificity and strength regions are indicated. The sequence LOGO of the consensus Dll-binding site (mainly composed of a TAAT motif), as determined from selection in bacteria [52], is shown in the left side. The positions of 11 TAAT/ATTA motifs within the LAE are indicated by vertical lines, and the corresponding DNA probes (#1–9) used in the EMSA experiments indicated above. Of note, all sites but one (probe #5) are situated within the CR1–3 conserved regions. LAE sequences (in grey) included in each labelled double-stranded DNA probe are indicated beneath, with mutated nucleotides shown in red. PhosphorImager detection of DNA-protein complexes separated by electrophoresis on native polyacrylamide gels is shown on the right. In-vitro translated Dll was omitted or added, as indicated above the lanes, numbered according to the tested probe. The positions of non- and Dll-specific shifted DNA-protein complexes are indicated by asterisks and a horizontal arrow, respectively. The extended probes #6–9 included the overlapping DNA fragments #1–2. In contrast to the two singly-mutated probes (#8–9), the high-affinity Dll-specific complex detected with the wild-type sequence (#6) was no longer detected with the doubly-mutated derivative (#7). (C) The triple TAAT-containing sequence within CR1 is critical for LAE activity in-vivo. GFP expression (green) alone and in combination with Bab2 immunostaining (red) of leg (F–F′) and antennal (G–G′) imaginal discs from a late third-instar larva expressing the H4-GFP reporter construct, a LAE-GFP derivative mutated on the three CR1 TAAT/ATTA motifs (identical to EMSA probe #7), are shown. No GFP expression could be detected, either in leg or in antennal tissues.