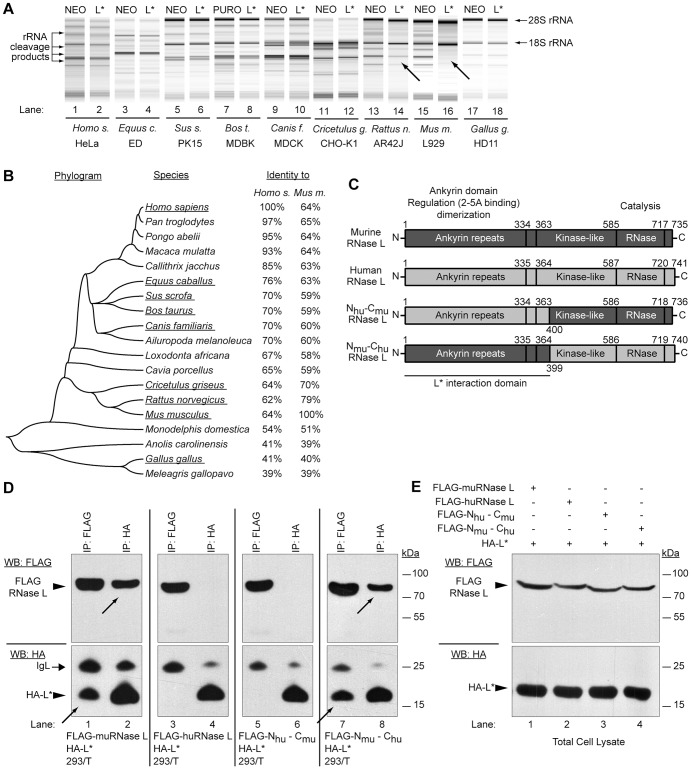
Figure 6. TMEV L* protein interacts with the N-terminal part of RNase L and is species specific.
A. L* acts in a species-specific fashion: Indicated cell lines derived from different species were transduced with empty (Neo) or with L*-expressing lentiviruses and subsequently transfected with 2–5A to activate RNase L. RNA degradation was assessed by RNA chips. Arrows indicate samples where L* provided protection. B. Mid-point rooted neighbor-joining tree inferred from published RNase L protein sequences. Evolutionary distances were calculated using the Poisson correction method and a single bootstrapped consensus tree based on 1000 replicates is represented. Underlined species were tested for L*-mediated RNase L inhibition. C. Schematic representation of mouse, human and chimeric RNase L. Conserved domains of RNase L and their functions are indicated. D–E. 293/T cells were cotransfected with the chimeric constructs and total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG (RNase L) and anti-HA (L*) antibodies (D). Total cell lysates corresponding to 5% of the input used for immunoprecipitations were analyzed as controls (E). Samples were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblot analysis with indicated antibodies (WB:FLAG or WB:HA). Arrows point to coimmunoprecipitated proteins. IgL: immunoglobulin light chain.