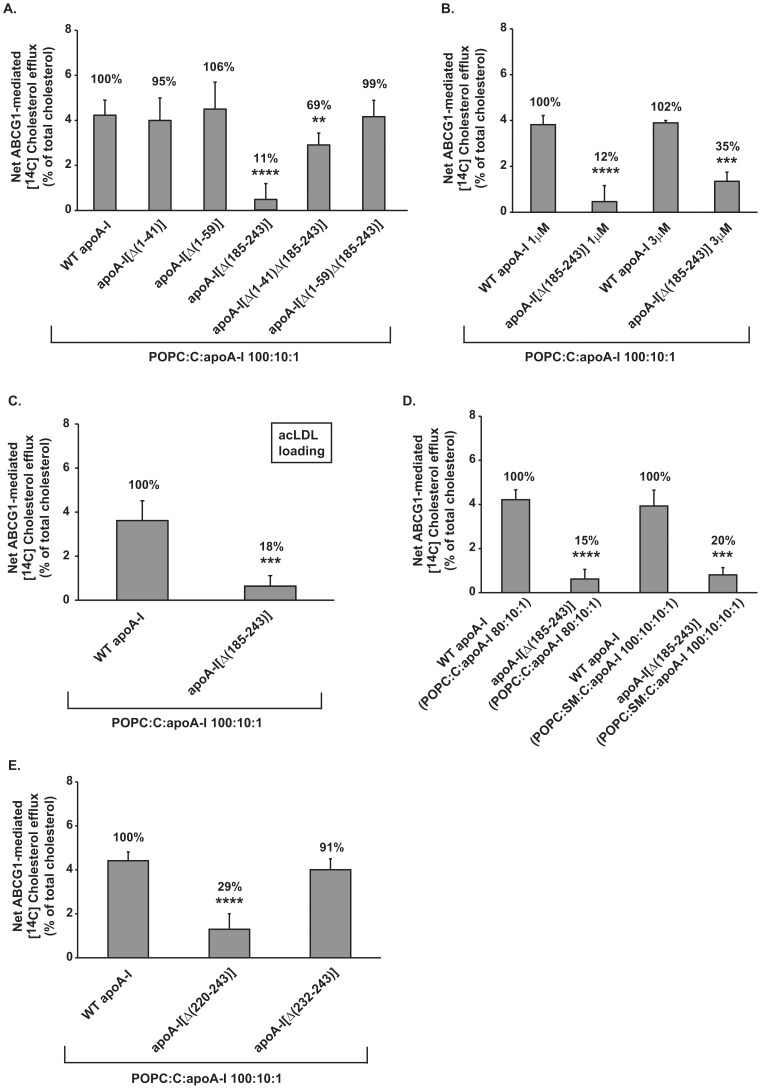
Figure 2. Effect of amino-, carboxyl-terminal deletions or double deletions of both the amino- and carboxy-terminal regions of apoA-I bound to rHDL particles on ABCG1-mediated cholesterol efflux from HEK293 cells transfected with an ABCG1-expressing plasmid.
HEK293 cells were transfected with empty vector (mock) or with ABCG1-expressing plasmid, labeled with [14C]cholesterol (A, B, D, E) or [14C]cholesterol and 30 µg/ml acLDL (C) for 24 h and then incubated with rHDL containing WT or mutants apoA-I forms, at a concentration of 1 µM apoA-I (A-E) or 3 µM apoA-I (B), for 4 h. rHDL particles have various lipid (POPC, SM, C):apoA-I ratios as indicated in each panel. The net ABCG1-mediated [14C]cholesterol efflux is calculated as described in Figure 1. (A) Values are the means ± SD from six (A, E) or three (B) independent experiments performed in duplicate or two (C, D) independent experiments performed in triplicate. **, p < 0.01 vs WT apoA-I; ***, p < 0.001 vs WT apoA-I; ****, p ≤ 0.0001 vs WT apoA-I. POPC, 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-L-phosphatidylcholine; C, cholesterol; SM, sphingomyelin.