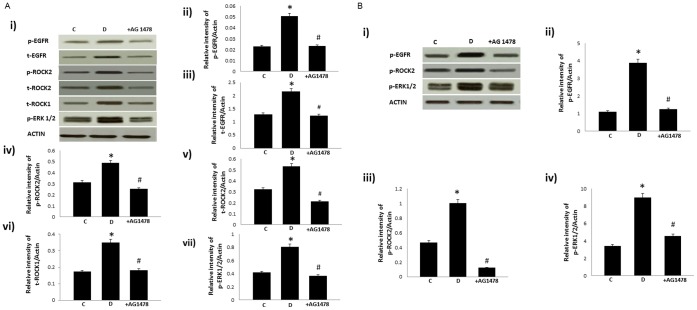
Figure 5. Chronic (A) or acute (B) treatment with AG1478, a selective inhibitor of EGFR, attenuates diabetes-induced elevation in ROCK and ERK1/2 signaling in the mesenteric vascular bed.
A) Panel i) is a representative western blot showing total (t−) or phosphorylated (p−) levels of the stated proteins in the isolated mesenteric bed from normal controls (C), diabetic (D) and diabetic animals treated for 4 weeks with AG1478 (1 mg/kg/alt-diem; +AG825); Panels ii–vii) are densitometry histograms showing total (t-) or phosphorylated (p−) levels of the stated proteins normalized to actin. B) Panel i) is a representative western blot showing phosphorylated (p−) levels of the stated proteins in the isolated mesenteric bed from normal controls (C), diabetic (D) and diabetic animals treated for 4 weeks with AG1478 (1 mg/kg/alt-diem; +AG825); Panels ii–iv) are densitometry histograms showing phosphorylated (p−) levels of the stated proteins normalized to actin. N = 5; Mean±SD. Asterisk (*) indicates significantly different (p<0.05) mean values from normal non-diabetic rats (C) whereas hash (#) indicates significantly different mean values (p<0.05) from diabetic rats (D).