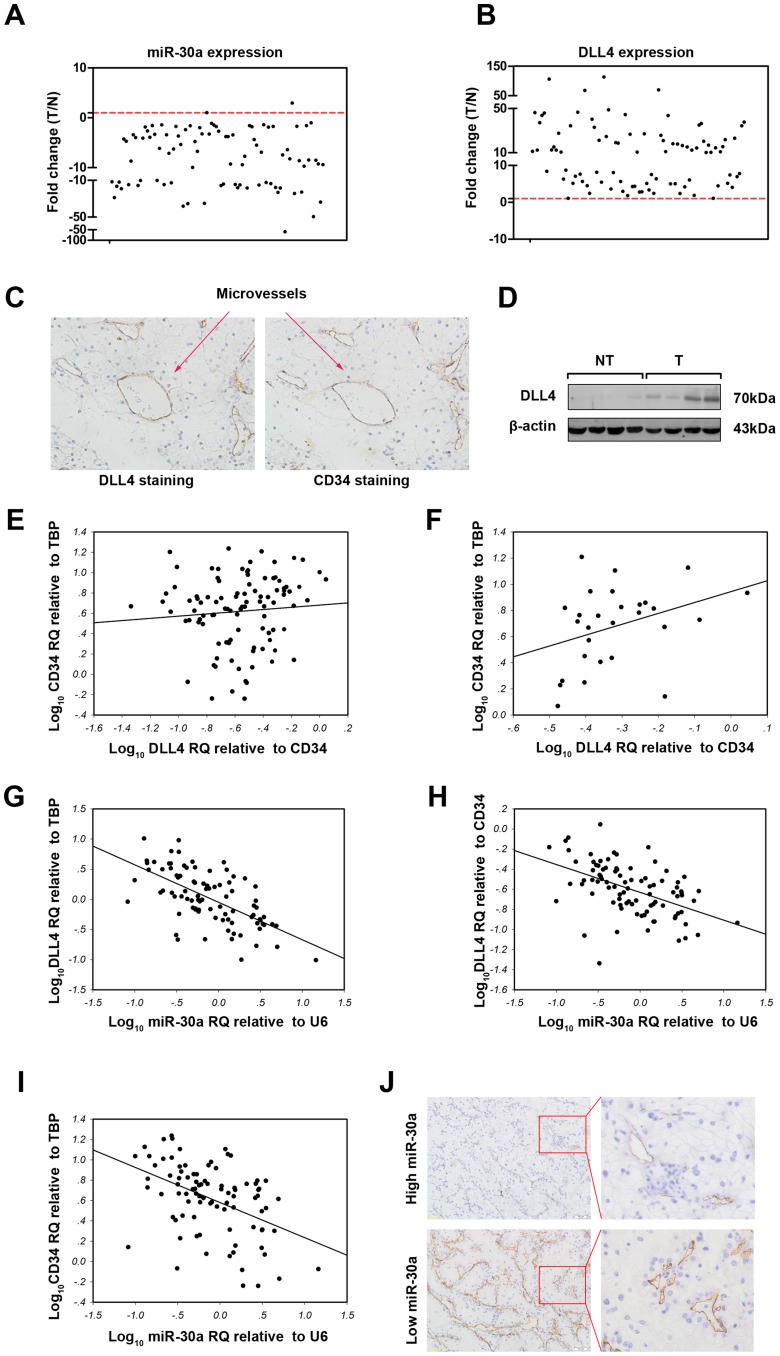
Figure 3. Associations of DLL4 and miR-30a expression with MVD in ccRCC.
The expressions of miR-30a (A) and DLL4 (B) in 90 cases of ccRCC and 28 cases of adjacent non-tumor tissues were examined by real-time PCR using U6 and TBP as the internal controls, respectively. Each case of ccRCC was further normalized to the mean levels of 28 cases of adjacent non-tumor tissues. (C) Immunohistochemical staining showed that DLL4 was mainly expressed in the endothelium of ccRCC angiogenesis. (D) Western blotting showed that DLL4 expression was significantly higher in RCC (T) than in adjacent non-tumor tissues (NT). (E) MVD represented by CD34 showed no association with DLL4 density (normalized to CD34, r = 0.452, p = 0.080). The gene expression levels in each ccRCC sample were log10 transformed before linear correlation analysis was performed. (F) MVD was positively correlated with DLL4 density in about 30% of ccRCC samples (n = 28) with the highest DLL4 density (Spearman correlation analysis, coefficient = 0.388, p = 0.042). (G) DLL4 expression was inversely correlated with miR-30a expression in ccRCC (linear correlation analysis, r = -0.632, p<0.001). (H) DLL4 density (normalized to CD34) was also inversely correlated with miR-30a expression in ccRCC (linear correlation analysis, r = -0.493, p<0.001). (I) CD34 expression (MVD) was inversely correlated with miR-30a expression in ccRCC (linear correlation analysis, r = -0.454, p<0.001). (J) miR-30a expression was divided into low or high levels at percentile of 70%. CD34-staining immunohistochemistry showed that less MVD in the high-level miR-30a group than in the low-level miR-30a group.