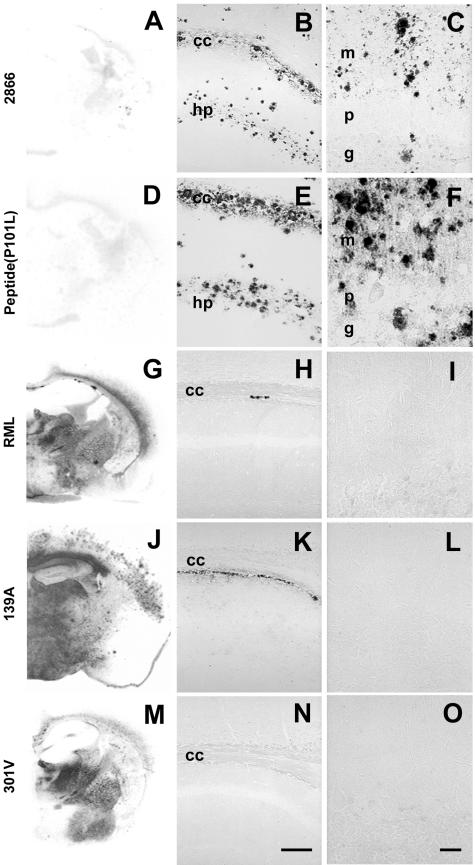
FIG.2.
GSS-like neuropathological features in the absence of PK-resistant PrPSc in spontaneous and synthetic peptide-induced prion disease in Tg mice expressing the MoPrP(P101L) allele. The analyzed brains are from Tg(MoPrP,P101L)196/Prnp0/0 mice inoculated with prions from spontaneously ill Tg(MoPrP,P101L)2866/Prnp0/0 mice (A, B, and C), β-rich MoPrP(89-143,P101L) peptide (D, E, and F), or for comparison, with RML (G, H, and I), 139A (J, K, and L), or 301V (M, N, and O) prions. Distribution of rPrPSc was determined by histoblotting (A, D, G, J, and M), and PrP-immunoreactive plaques were detected by hydrolytic autoclaving in the hippocampus (B, E, H, K, and N) and cerebellum (C, F, I, L, and O). Abbreviations: cc, corpus callosum; g, granule cell layer; hp, stratum radiatum of the CA1 region of the hippocampus; m, molecular layer; p, Purkinje cell layer. The bar in panel N represents 100 μm and applies to panels B, E, H, and K; The bar in panel O represents 30 μm and applies to panels C, F, I, and L.