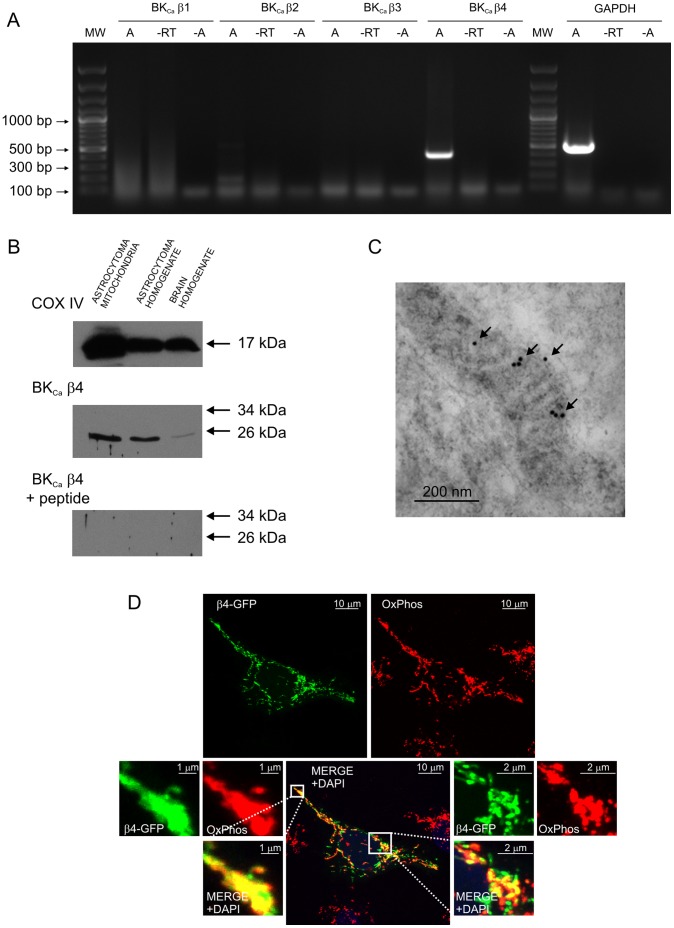
Figure 2. Localization of the BKCa channel regulatory β4 subunit in astrocytoma mitochondria.
A. Detection of mitoBKCa channel regulatory β4 subunit mRNA in astrocytoma cells. The BKCa subunit β4 mRNA was detected at a size of 405 bp. No products were obtained for the BKCa subunits β1, β2 and β3. GAPDH served as a positive control and was detected at a size of 496 bp. The negative control without reverse transcriptase (−RT) and samples without cDNA (−A) had no signals. The results presented are representative of seven independent experiments. B. Immunoblot of astrocytoma mitochondria, astrocytoma cell homogenate and brain homogenate fractions labeled with the anti-BKCa channel β4 subunit antibody. A control antigen (BKCa β4+ peptide) was used as a positive control for the specificity of the antibody. An anti-cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV antibody (COX IV) was used as a mitochondrial marker (n = 3). C. Immuno-gold electron microscopy localization of the BKCa channel β4 regulatory subunit in mitochondria of cultured human astrocytoma cells. The β4 subunit molecules were labeled using 10 nm colloidal-gold particles (arrows). D. High-power confocal image of cultured astrocytoma cells immunolabeled to detect OxPhos (red) and β4-GFP-transfected cells (green). The superimposition of the two signals revealed the mitochondrial localization of BKCa β4 in human astrocytoma cells (yellow). The DNA-binding dye DAPI was used to stain the cell nuclei (blue). For details concerning the astrocytoma cells, see the Materials and Methods.