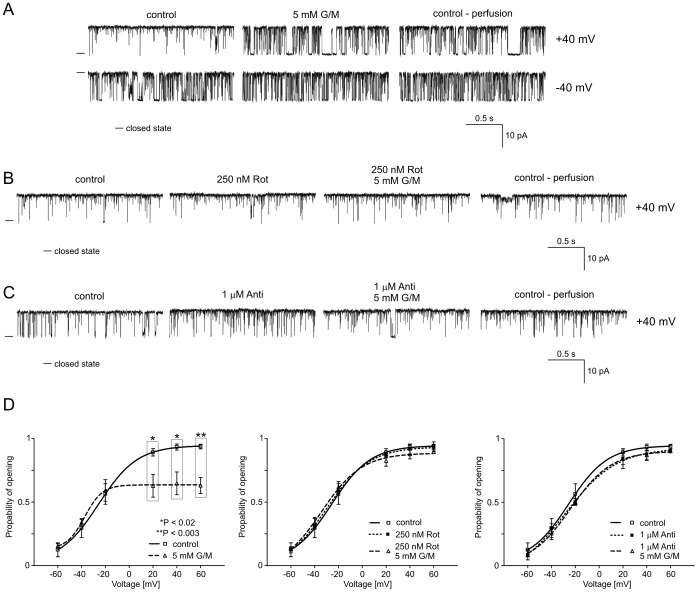
Figure 4. Glutamate/malate reduces the Po of the mitochondrial large-conductance Ca2+-regulated potassium channel at positive voltages.
A. Single-channel recordings of the mitoBKCa channel activity in symmetric 150/150 mM KCl isotonic solution (200 µM Ca2+) at +40 and −40 mV under control conditions, after the addition of 5 mM glutamate/malate (G/M) and after perfusion. B. Single-channel recordings of the mitoBKCa channel activity in symmetric 150/150 mM KCl isotonic solution (200 µM Ca2+) at +40 mV under control conditions, after the addition of 250 nM rotenone (Rot) and 5 mM G/M plus 250 nM Rot and after perfusion. C. Single-channel recordings of the mitoBKCa channel activity in symmetric 150/150 mM KCl isotonic solution (200 µM Ca2+) at +40 mV under control conditions, after the addition of 1 µM antimycin A (Anti) and 5 mM G/M plus 1 µM Anti and after perfusion. D. Analysis of the probability of channel opening at voltages ranging from −60 to +60 mV under the conditions described in A, B and C. *P<0.02 and **P<0.003 vs. the control.