FIG. 4.
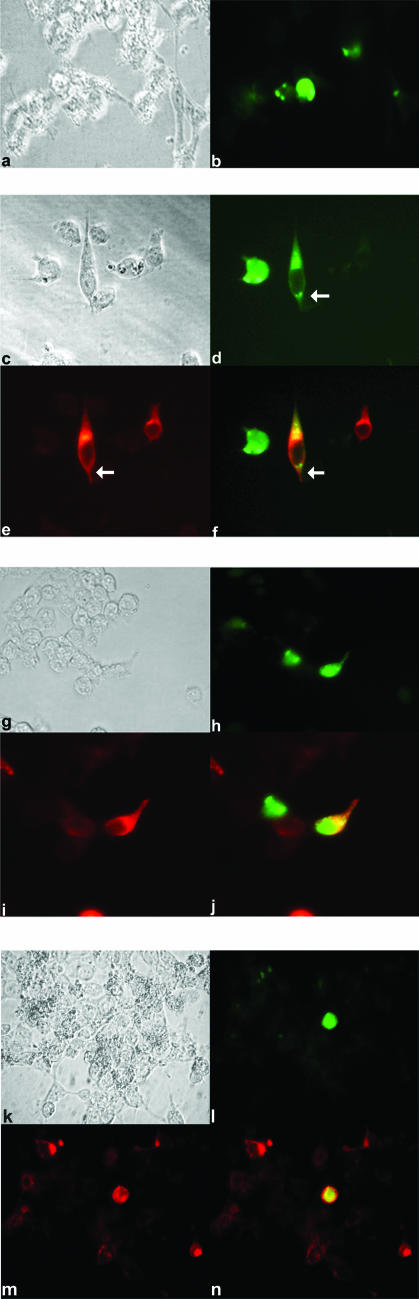
K1 promotes cytoplasmic localization of FKHR. (a) 293 cells were transfected with empty vector (EF) and FKHR-GFP. Transfected cells were fixed and examined by bright-field microscopy. (b) The same cells as in panel a examined for expression and distribution of FKHR-GFP (green) by immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells expressing FKHR-GFP appear to be undergoing apoptosis based on their rounded morphology. (c) Cells were transfected with EF-K1 and FKHR-GFP expression plasmids. (d) The same cells as in panel c fixed and examined for expression and distribution of FKHR-GFP (green). (e) The same cells as depicted in panels c and d stained for expression of K1 (red) and examined by immunofluorescence microscopy. (f) Merged image of the same cells shown in panels c, d, and e. Yellow represents the colocalization of K1 (red) and FKHR-GFP (green). The white arrow indicates a cell that is coexpressing K1 and FKHR-GFP. The adjacent cell to its left expresses FKHR-GFP, but not K1, and appears to be undergoing apoptosis. (g) Cells were transfected with EF-K1 and the mutant FKHRAAA-GFP expression plasmid. (h) The same cells shown in panel g analyzed for expression and distribution of FKHRAAA-GFP (green). Based on their morphology, these cells appear to be undergoing apoptosis. (i) Cells were examined for expression of K1 (red) by immunofluorescence microscopy. (j) Merged image of the same cells shown in panels g, h, and i. Yellow represents the colocalization of FKHRAAA-GFP (green) and K1 (red). (k) Cells were transfected with FKHR-GFP and the EF-K1ITAM− expression plasmid. Transfected cells were fixed and examined by bright-field microscopy. (l) The same cells shown in panel k analyzed for expression and distribution of FKHR-GFP (green). (m) Cells were examined for expression of the K1ITAM− mutant (red). (n) Merged image of the same cells shown in panels k, l, and m. Yellow represents the colocalization of FKHR-GFP (green) and the K1ITAM− mutant (red).