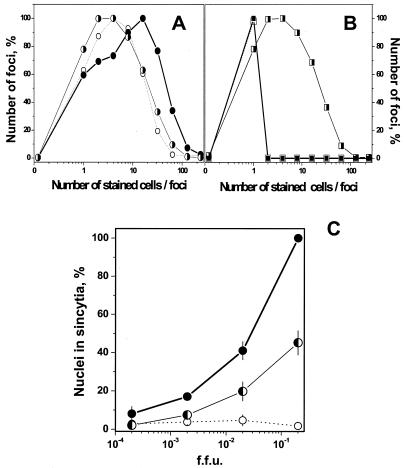
FIG. 4.
(A and B) Spreading of VHSV infection at low pH after adjustment of pH to 7.5. VHSV-infected EPC cell monolayers (MOI of 0.01) were incubated for 24 h. The medium pH was then changed, and the cells were incubated for a further 24 h and stained 48 h after the beginning of the infection. When the medium was changed, monolayers at pH 7.5 were adjusted to pH 6.5 (A) and monolayers at pH 6.5 were adjusted to pH 7.5 (B). The number of foci at each focus size (number of stained cells per foci) was counted and expressed as number of foci per each focus size/total number of foci counted × 100. ○, 24 h at pH 7.5; •, 24 h + 24 h at pH 7.5; ◑, 24 h at pH 7.5 + 24 h at pH 6.5; □, 24 h at pH 6.5; ▪, 24 h + 24 h at pH 6.5; ◨, 24 h at pH 6.5 + 24 h at pH 7.5. (C) Syncytium formation of VHSV-infected EPC cells at pH 7.5 and 6.5. VHSV-infected EPC cell monolayers (MOI of 0.01) were incubated for 12 h. The medium pH was changed, and cells were incubated 12 h more and stained 24 h after the beginning of the infection. When the medium was changed, monolayers at pH 6.5 were adjusted to pH 7.5 and those at 7.5 were adjusted to pH 7.5 or 6.5. To assay for syncytium formation, the cultures were exposed to fusion medium at pH 6 for 30 min at 14°C, and the medium was changed to pH 7.5 and incubated for a further 2 h at 20°C. Results are expressed as the percentage of nuclei in syncytia as determined by the formula number of nuclei in syncytia/total number of nuclei × 100. Averages and standard deviations from two different experiments, each performed in triplicate, are given. •, 12 h + 12 h at pH 7.5; ○, 12 h + 12 h at pH 6.5; ◐, 12 h at pH 6.5 + 12 h at pH 7.5.