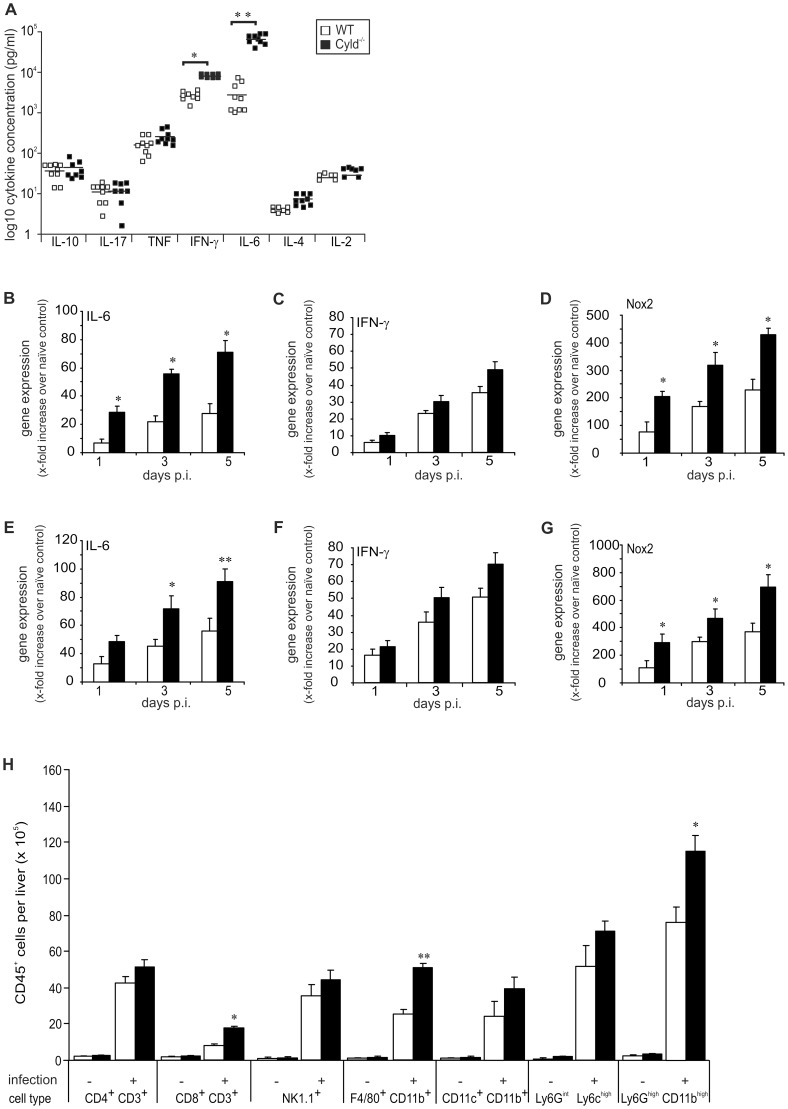
Figure 2. CYLD impairs IL-6 and IFN-γ production and leukocyte recruitment in listeriosis.
(A) The serum concentrations of IL-10, IL-17, TNF, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-2 were determined in Lm-infected WT and Cyld−/− mice by a cytometric bead assay at day 5 p.i. (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01). Symbols represent individual mice from two representative experiments. (B–G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of hepatic (B–D) and splenic (E–G) IL-6, IFN-γ, and NOX2 mRNA expression. Data show the increase of the respective mRNA expression of Lm-infected over uninfected mice of the same mouse strain. Data represent the mean ± SD of 5 mice. Data from of two representative experiments are shown. (H) The number of different leukocyte populations was determined in cells isolated from livers of uninfected and Lm-infected WT and Cyld−/− mice. Data show the mean ± SD of CD45+ cell populations from 5 mice per experimental group. Data from one of two representative experiments are shown (* p<0.05 and ** p<0.001 for WT vs. Cyld−/− mice).