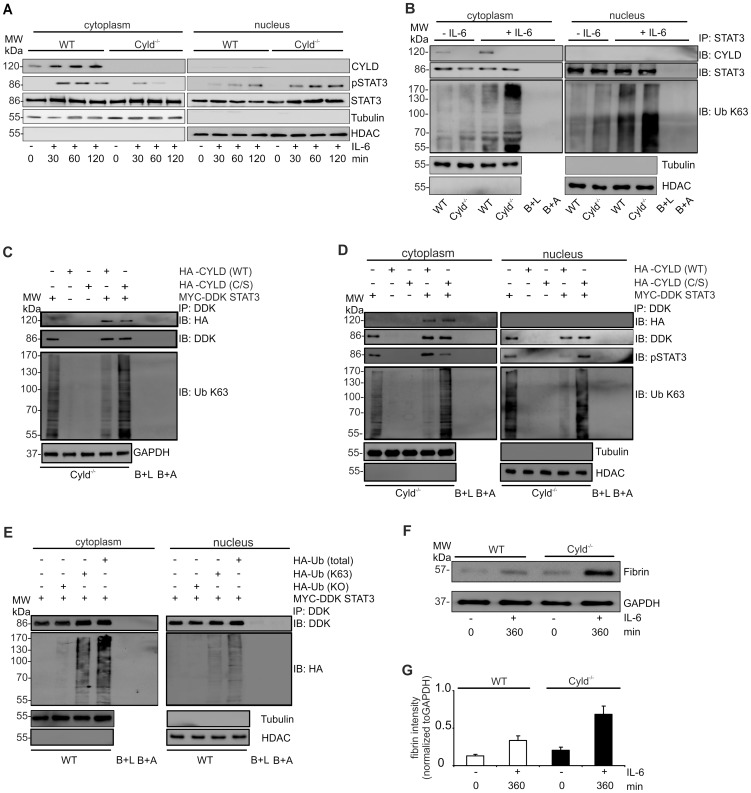
Figure 4. CYLD binds to STAT3 and inhibits nuclear accumulation of activated STAT3 and fibrin production in hepatocytes.
(A) Proteins were isolated from the cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively, of WT and Cyld−/− hepatocytes. WB were stained with α-tubulin and α-histone deacetylase (HDAC) as marker proteins for the cytoplasm and nucleus, respectively. (B) Cytoplasmic and nuclear protein lysates of unstimulated and IL-6-stimulated (200 ng/ml) WT and Cyld−/− hepatocytes were immunoprecipitated with STAT3. Immunoprecipitates were stained for CYLD, STAT3, and K63-linked ubiquitin. The purity and amount of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins was controlled by staining lysates for tubulin and HDAC, respectively, before immunoprecipitation. Beads plus lysate without antibody before immunoprecipitation (B+L) and beads plus STAT3 antibody without lysates (B+A) were used as controls. (C, D) Cyld−/− hepatocytes were transfected with MYC-DDK STAT3, HA-CYLD (WT), mutant HA-CYLD (C/S) lacking catalytic activity as indicated. After IL-6 stimulation (1 h), total (C), cytoplasmic (D) and nuclear (D) lysates were immunoprecipitated with α-DDK. Immunoprecipitates were stained for the indicated proteins. (E) WT hepatocytes were transfected with MYC-DDK STAT3, ubiquitin with all lysine residues (HA-Ub total), ubiquitin with K63 only (HA-Ub K63), and ubiquitin with no lysine residues (HA-Ub KO) as indicated. After IL-6 stimulation (1 h), cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were isolated and immunoprecipitated with α-DDK. Immunoprecipitates were stained for the indicated proteins. (F) WB analysis of fibrin production in unstimulated (0 min) and IL-6 stimulated (360 min) cultivated WT and Cyld−/− hepatocytes. (G) Quantification of fibrin (± SD) was performed from WB data of unstimulated and IL-6-stimulated WT and Cyld−/−, respectively, hepatocytes. Representative results from one of three experiments are shown.