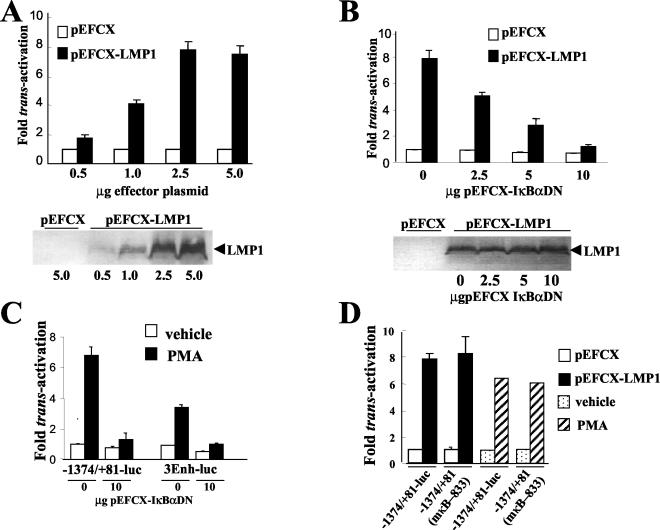
FIG.1.
LMP1 and PMA transactivate the bfl-1 promoter in DG75 cells by mechanism(s) that are dependent upon the transcription factor NFκB; transactivation does not require a previously identified NF-κB-binding site at position −833/−823 relative to the transcription start site. (A) Dose-dependent transactivation of the bfl-1 promoter by LMP1. DG75 cells were cotransfected with increasing amounts of either pEFCX or pEFCX-LMP1 (effector plasmids) and 2.5 μg of −1374/+81-Luc. Cells were harvested at 24 h posttransfection and analyzed for luciferase activities, which were then normalized for transfection efficiency (based on β-galactosidase activity measured from cotransfected pCMVlacZ reporter, which was included in all transfections). Luciferase values obtained by cotransfection with pEFCX were arbitrarily assigned a value of 1.0 and activation represents the relative normalized luciferase activities obtained upon cotransfection with the effector plasmids with the quantities indicated. Selected extracts from these transfections were analyzed for LMP1 expression by Western blotting (shown underneath). (B) Inhibition of LMP1-mediated activation of the bfl-1 promoter by overexpression of a superrepressor mutant form of IκBα (IκBαDN). DG75 cells were cotransfected with 2.5 μg of pEFCX-LMP1 or empty vector pEFCX and 2.5 μg of −1374/+81-Luc together with various amounts (0, 2.5, 5.0, or 10.0 μg) of pEFCX-IκBαDN. Cells were harvested at 24 h posttransfection, and luciferase values were measured, normalized as above, and presented as activation (n-fold) over control (empty vector in the absence of expression of IκBαDN equals 1). Selected extracts from these transfections were analyzed for LMP1 expression by Western blotting (shown underneath). (C) PMA activates the bfl-1 promoter in an NF-κB-dependent manner. DG75 cells were transfected with either 2.5 μg of −1374/+81-Luc or 3Enh-Luc in the presence or absence of 10.0 μg of pEFCX-IκBαDN and then treated with either 10−7 M PMA or vehicle control (0.062% ethanol) at 18 h posttransfection. Cells were harvested at 24 h posttreatment, and the normalized luciferase values obtained are presented as increases (n-fold) over control values. The values obtained with transfected cells that had been treated with vehicle control were arbitrarily assigned a value of 1. (D) Neither LMP1- nor PMA-mediated activation of the bfl-1 promoter requires the known NF-κB-binding site at position −833/−823 in the bfl-1 promoter. DG75 cells were cotransfected with 2.5 μg of pEFCX-LMP1 or empty vector pEFCX and 2.5 μg of −1374/+81-Luc or its NF-κB-mutated derivative −1374/+81(mκB-833)-Luc. In the PMA study, DG75 cells were transfected with 2.5 μg of −1374/+81-Luc or 1374/+81(mκB-833) and then treated with either 10−7 M PMA or vehicle control (0.062% ethanol) at 18 h posttransfection. Cells were harvested at 24 h either posttransfection or posttreatment (PMA or vehicle, respectively) and assayed for luciferase activity. Normalized luciferase values were expressed as activation (n-fold) over control empty vector or vehicle as appropriate.