Figure 1.
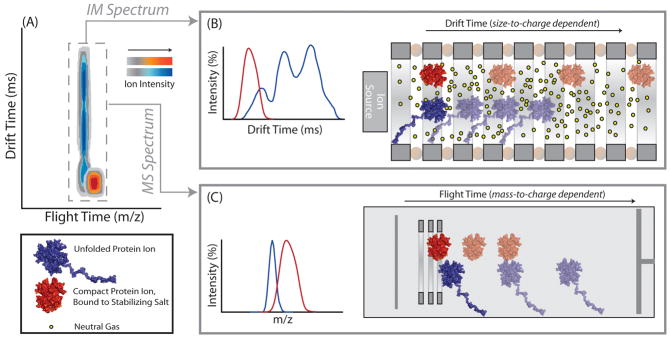
A schematic diagram of the IM-MS experiment, in which collisional heating of two protein complexes has generated different CIU responses. A) IM-MS data is multi- dimensional, consisting of IM drift time (in ms), m/z (measured in a time-of-flight mass analyzer), and ion intensity (shown on a color axis, different for the two ion populations). Signal corresponding to stabilizing salt-bound protein is illustrated on a red color axis, and a blue color axis corresponds to signal from protein ions in the absence of stabilizing salt adducts. B) Equally-charged protein ions are separated in a travelling-wave type IM separator based on their conformational differences following CIU. Protein ions bound to stabilizing salts travel more quickly in the IM separator when compared to non-stabilized protein ions due to their more-compact, folded geometry. IM data for unfolded proteins typically reveal a multimodal drift time profile, indicative of multiple unfolded intermediate states, stable on the time scale of the experiment, created during the CIU process C) Subsequent mass analysis of ions using a time-of-flight mass analyzer reveals that salt molecules remain bound to protein ions during the analysis, resulting in an increased molecular mass for stabilized complexes.
