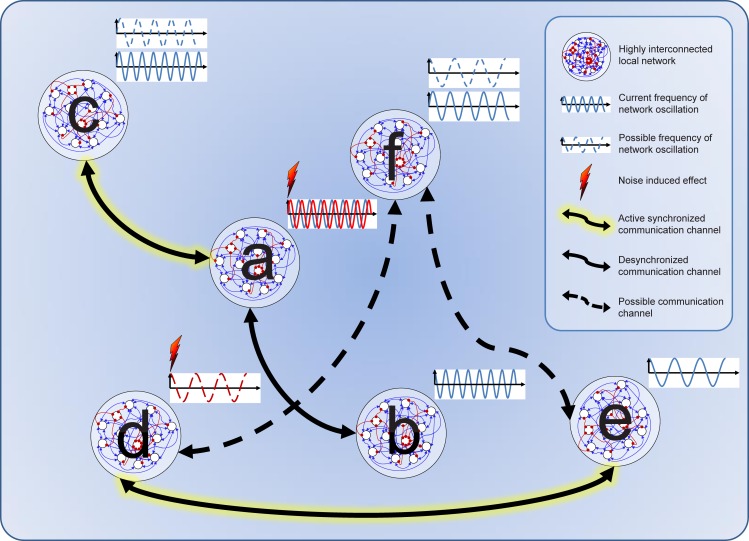
Figure 1.
Cartoon of network dynamics showing noise induced switching of transient communication channels. At start, a network is synchronized with network b. Noise than induces a phase shift in b, thus desynchronizing this channel and synchronizing a with c. Noise can also induce oscillation in d synchronizing it with e. F Could principally also synchronize with d and e, but is currently in its different oscillation mode.