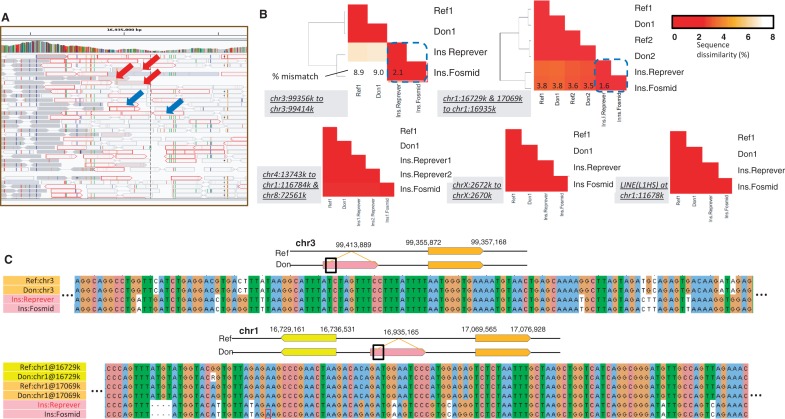
Figure 3.
Reconstruction of fosmid-validated duplications. Totally 1000 simulated genomes are constructed and underwent random (A) (discordant) paired-end reads mapped around a validated insertion site chr1:16935160 (from chr1:17069565–17076928 and chr1:16729161–16736531). There are only a few discordant reads that bridge the insertion site to its template (red arrows). Reprever automatically recruits neighboring orphan reads (blue arrows) to increase read coverage for reconstruction. (B) Comparison of reconstructed and true (fosmid) insertion sequences. The reconstructed sequences (Ins.Reprever) are much closer to the true insertions (Ins.fosmid) compared with the template sequences (Ref1 and Ref2). Reconstructed donor sequences at the template sites (Don1, Don2) are almost identical to the templates. (C) Multiple sequence alignment visualization of sequence variation between templates and reconstructed sequences. Highly varied regions including deletions are reconstructed perfectly.
automatically recruits neighboring orphan reads (blue arrows) to increase read coverage for reconstruction. (B) Comparison of reconstructed and true (fosmid) insertion sequences. The reconstructed sequences (Ins.Reprever) are much closer to the true insertions (Ins.fosmid) compared with the template sequences (Ref1 and Ref2). Reconstructed donor sequences at the template sites (Don1, Don2) are almost identical to the templates. (C) Multiple sequence alignment visualization of sequence variation between templates and reconstructed sequences. Highly varied regions including deletions are reconstructed perfectly.