Table 4.
Estimates 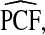
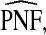
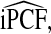 and
and 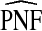 (with 95% bootstrap confidence intervals in parenthesis) based on the observed distribution of risks R and outcome data for CRC in AARP women
(with 95% bootstrap confidence intervals in parenthesis) based on the observed distribution of risks R and outcome data for CRC in AARP women
| p | PCF* | 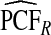 |
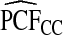 |
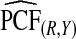 |
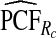 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.178 | 0.245 (0.244, 0.246) | 0.178 (0.155, 0.202) | 0.178 (0.152, 0.205) | 0.179 |
| 0.20 | 0.313 | 0.415 (0.413, 0.416) | 0.313 (0.284, 0.342) | 0.311 (0.277, 0.345) | 0.307 |
| 0.30 | 0.423 | 0.551 (0.549, 0.552) | 0.420 (0.387, 0.452) | 0.420 (0.377, 0.462) | 0.418 |
| 0.40 | 0.549 | 0.663 (0.662, 0.664) | 0.547 (0.515, 0.579) | 0.547 (0.500, 0.594) | 0.518 |
| q |
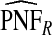 , , 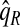
|
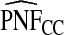 |
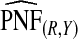 , , 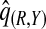
|
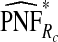 , , 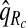
|
|
| 0.90 | 0.711 (0.710, 0.712), 0.832 | 0.797 (0.784, 0.810) | 0.797 (0.737, 0.858), 0.898 | 0.857, 0.927 | |
| 0.80 | 0.556 (0.555, 0.557), 0.704 | 0.660 (0.641, 0.679) | 0.661 (0.600, 0.723), 0.800 | 0.725, 0.839 | |
| 0.70 | 0.438 (0.437, 0.439), 0.585 | 0.543 (0.518, 0.569) | 0.545 (0.490, 0.599), 0.691 | 0.602, 0.751 | |
| 0.60 | 0.342 (0.341, 0.343), 0.473 | 0.446 (0.418, 0.473) | 0.447 (0.393, 0.501), 0.597 | 0.488, 0.635 | |
| p | 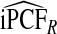 |
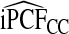 |
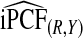 |
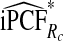 |
|
| 0.10 | 0.667 (0.666, 0.668) | 0.592 (0.589, 0.596) | 0.592 (0.575, 0.609) | 0.572 | |
| 0.20 | 0.634 (0.633, 0.634) | 0.568 (0.565, 0.572) | 0.567 (0.552, 0.582) | 0.547 | |
| 0.30 | 0.585 (0.585, 0.586) | 0.530 (0.527, 0.533) | 0.530 (0.517, 0.543) | 0.511 | |
| 0.40 | 0.524 (0.524, 0.525) | 0.482 (0.479, 0.486) | 0.483 (0.472, 0.493) | 0.464 | |
| q | 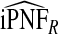 |
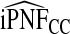 |
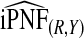 |
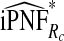 |
|
| 0.90 | 0.083 (0.082, 0.083) | 0.086 (0.084, 0.089) | 0.086 (0.084, 0.089) | 0.093 | |
| 0.80 | 0.145 (0.145, 0.146) | 0.160 (0.154, 0.165) | 0.160 (0.154, 0.165) | 0.172 | |
| 0.70 | 0.195 (0.195, 0.195) | 0.216 (0.207, 0.224) | 0.216 (0.208, 0.225) | 0.238 | |
| 0.60 | 0.234 (0.233, 0.234) | 0.268 (0.258, 0.278) | 0.269 (0.259, 0.279) | 0.293 |
The corresponding observed proportion of cases PCF* found among the fraction q of the AARP population at highest risk and the proportions pR and pCC of cases found among the fractions 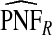 and
and 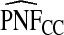 of the AARP population at highest risk are also shown.
of the AARP population at highest risk are also shown. 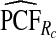 and
and 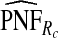 are based means over five test sets of the model after recalibration using 5-fold cross-validation.
are based means over five test sets of the model after recalibration using 5-fold cross-validation.
