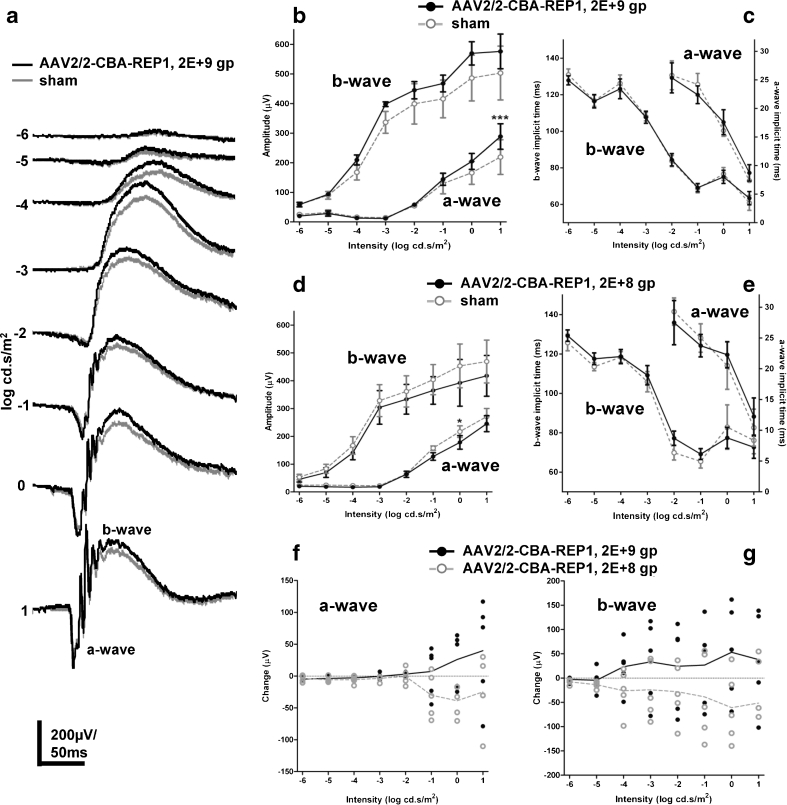
Fig. 6.
ERG analysis of Chm null/WT mice, treated with AAV2/2-CBA-REP1 and DMEM (sham). a Representative averaged ERG traces from high-dose (2 × 109 gp) AAV2/2-CBA-REP1-injected (shown in black) and sham-injected (shown in grey) eyes. b, c Quantification of the amplitude of a- and b-waves (b) and implicit time data (c) recorded across a range of stimulus intensities in high-dose (2 × 109 gp) AAV2/2-CBA-REP1-injected (filled black circles and solid black lines) and sham-injected (open grey circles and dashed lines) eyes. Plotted symbols show mean ± SEM, n = 5. d, e Quantification of the amplitude of a- and b-waves (d) and implicit time data (e) recorded across a range of stimulus intensities in low-dose (2 × 108 gp) AAV2/2-CBA-REP1-injected (filled black circles and solid black lines) and sham-injected (open grey circles and dashed lines) eyes. Plotted symbols show mean ± SEM, n = 5. f, g Change in a-wave (f) and b-wave (g) amplitude in high-dose (2 × 109 gp, filled black circles) and low-dose (2 × 108 gp, open grey circles) AAV2/2-CBA-REP1 treatment groups. Individual values shown as point and group means as connecting lines